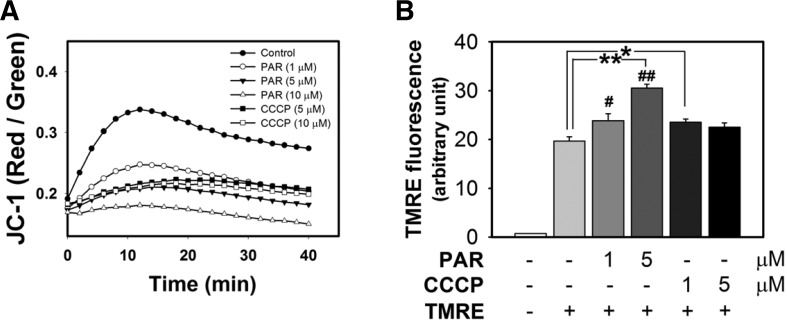
Fig. 5.
PAR polymer depolarizes mitochondrial membrane potential in isolated mouse brain mitochondria. (A) Measurement of PAR polymer-induced depolarization of mitochondria with JC-1. Isolated mouse brain mitochondria were preincubated with JC-1. After addition of PAR polymer or CCCP to mitochondria containing JC-1, real-time fluorescence intensity of JC-1 aggregates (red) and monomer (green) in the reaction mixture was measured using a fluorescence microplate reader. Dot and trace represented the mean of red- to green-fluorescence ratio. (B) Measurement of PAR polymer-induced depolarization of mitochondria with TMRE. Isolated mouse brain mitochondria were treated with PAR or CCCP for 10 min at 37°C prior to incubation with TMRE for an additional 10 min. After centrifugation, TMRE fluorescence in the supernatant of the reaction mixture was measured using a fluorescence microplate reader. Bar represents the TMRE fluorescent level in the supernatant (mean ± SEM). Significant difference to control was determined by one-way ANOVA (Duncan’s multiple range test, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01) or t-test (#P < 0.05).