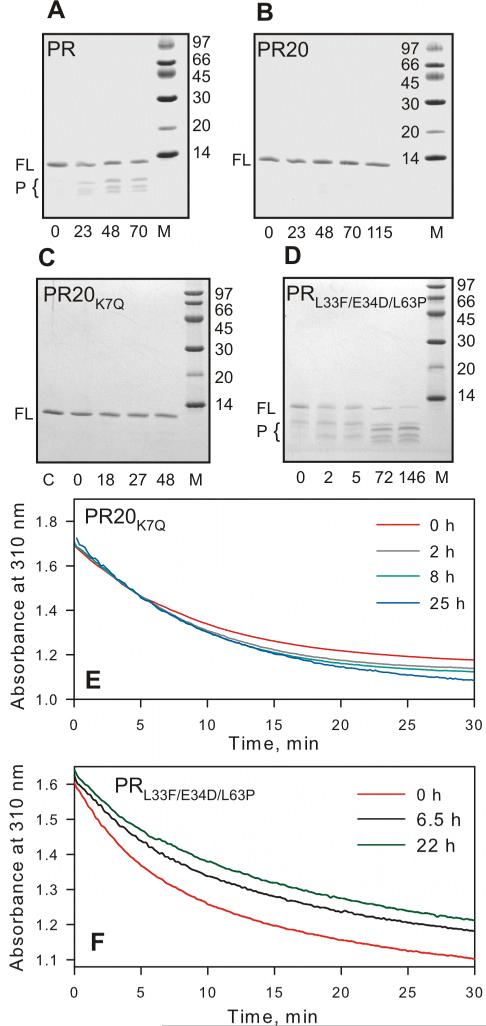
Figure 2.
Time course of autoproteolysis of (A) PR, (B) PR20, (C) PR20K7Q and (D) PRL33F/E34D/L63P at room temperature in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer, pH 5. Proteins were folded from 12 mM HCl by a quench protocol as previously described,25 to give a final concentration of 13 μM (as dimer) in 50 mM acetate, pH 5. Samples were withdrawn at the indicated times (in hours), mixed with gel loading buffer and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (20% homogeneous PhastGel, GE Healthcare). FL and P designate full length protease and products of autoproteolysis, respectively. M denotes molecular weight markers in kDa. Numbers below the gels denote hours of incubation at room temperature. (C and E) show that PR20 bearing the wild-type residue in position 7 (K7Q) is equally resistant to autoproteolysis as PR20. Sample PR20K7Q prior to initiating the assay is shown in lane C (panel C). (E and F) Time dependent decrease in protease mediated hydrolysis of substrate IV assayed at the indicated times at a final enzyme concentration of 440 nM for PR20K7Q and 330 nM PRL33F/E34D/L63P and final substrate concentration 380 μM, 28 °C. PRL33F/E34D/L63P shows a significant decrease in catalytic activity with increasing time of incubation, consistent with appearance of products of autoproteolysis, unlike PR20 or PR20K7Q (compare B and C with D). (D and F) demonstrate that mutations L33F and L63P are not responsible for the reduced rate of autoproteolysis seen with PR20 consistent with a rate comparable to wild-type PR.