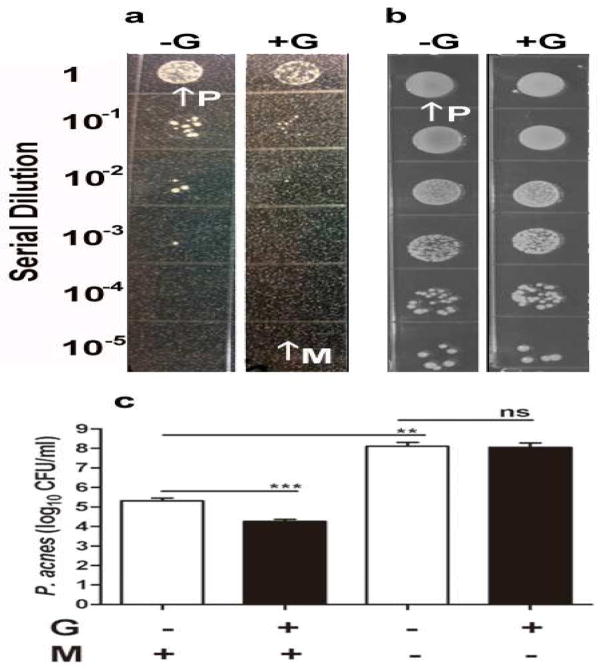
Figure 1. Inhibition of the growth of P. acnes by skin microorganisms in a homogeneous microbial lawn.
(a) A homogeneous lawn of microbes was created by pouring the skin microorganisms (M, arrow; 105 CFU) that were pre-mixed with 1% agar with/without glycerol (+G/-G; 20 g/l) in TSB. P. acnes (P, arrow) bacteria with a serial dilution (5 × 106- 5 × 101 CFU in 5 μl PBS) were spotted on the top of microbial lawn for three days for CFU counts. (b) The serially diluted P. acnes was spotted on the regular plates (without pouring skin microorganisms) with/without glycerol. (c) The CFU counts of P. acnes were presented as 95% CI of the means of three independent experiments. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 was obtained by two-tailed t-tests. ns, not significant.