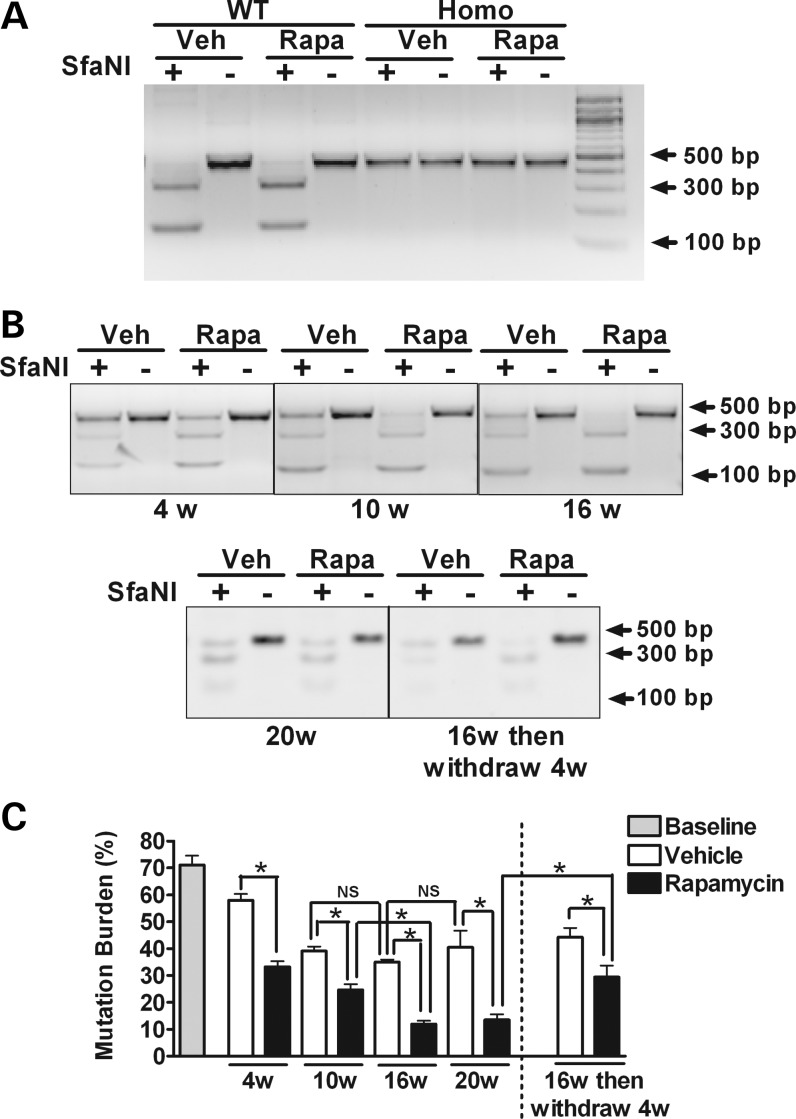
Figure 2.
Mutation levels determined by restriction fragment-length polymorphism analysis in WT, heteroplasmic and homoplasmic cybrid cells. WT, heteroplasmic and homoplasmic cybrid cells were treated with 20 nm rapamycin or vehicle for up to 20 weeks. Restriction digestion analyses with SfaNI were followed by densitometric analysis of digested bands for quantification of mutation levels. (A) Gel images demonstrate the cleavage pattern of a 450 bp mtDNA PCR product after digestion with SfaNI. In WT cybrid cells, the mtDNA PCR product is completely cleaved at nucleotide position (np) 11778, resulting in fragments of 308 and 142 bp. In contrast, in homoplasmic G11778A cybrid cells, the mutation eliminates the cleavage site, resulting in a single 450-bp band. As expected, in WT and in homoplasmic cybrid cells, these results are not altered by 16 weeks of treatment with rapamycin compared with vehicle-treated cell. (B) The cleavage pattern of mtDNA PCR product derived from heteroplasmic cybrid cells treated with 20 nm rapamycin or vehicle for 4, 10 16 and 20 weeks. The effect of rapamycin withdrawal also was evaluated in cells that had been treated for 16 weeks with rapamycin by growing them for an additional 4 weeks in media lacking rapamycin. (C) The percentage of mtDNA with the G11778A mutation was determined by the ratio of the intensities of the 450 bp PCR product after cutting with SfaNI to the same PCR products without cutting. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, and are analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. n = 4 separately treated dishes per set of conditions. *P < 0.05; NS, not significant.