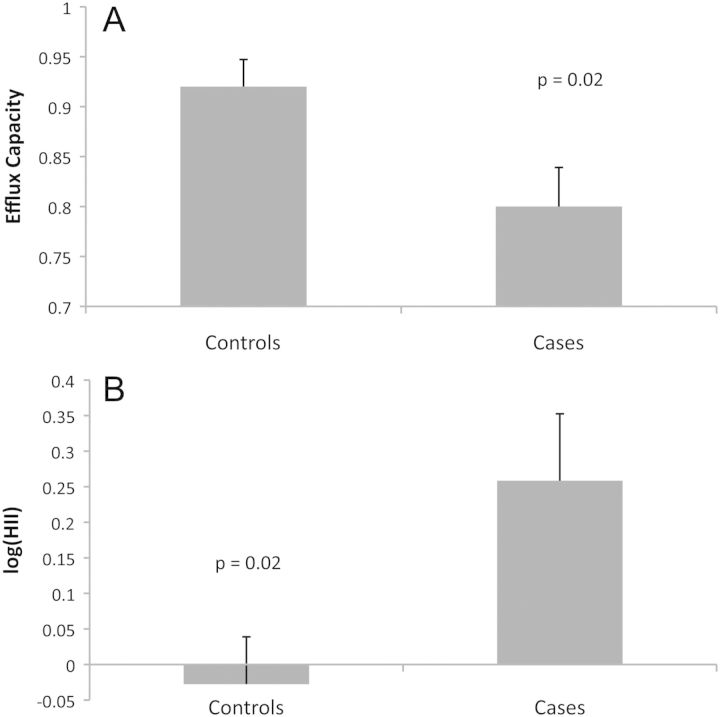
Figure 1.
Associations of the high-density lipoprotein inflammatory index (HII) and efflux capacity with heart failure (HF). HII values were skewed and were therefore log-transformed. Comparison of the mean HII in cases (ischaemic HF) and controls (no ischaemia, no HF) by the Student's t-test revealed a significant difference (0.26 vs. –0.028, P = 0.02). Efflux values were normally distributed, and comparison of means by the Student's t-test also showed a significant difference (0.80 vs. 0.92, P = 0.02). HF correlates with a high HII (impaired anti-oxidant capacity) and low efflux capacity ratio (reduced cholesterol efflux capacity). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.