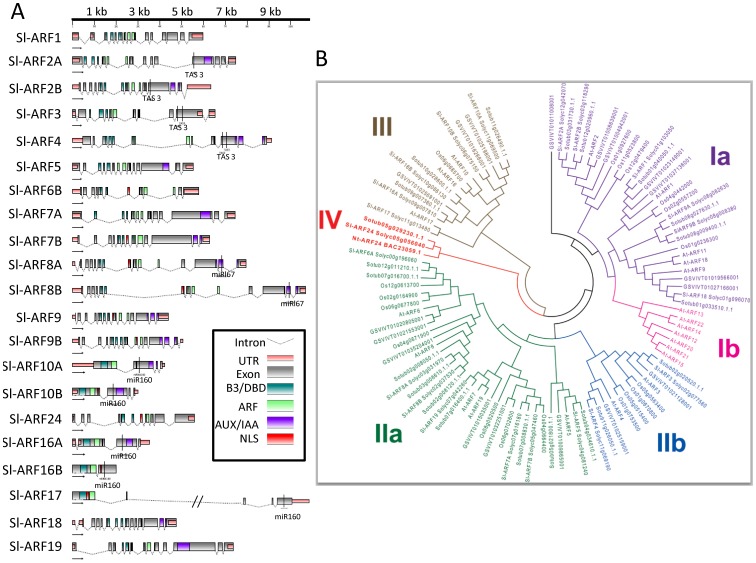
Figure 1. The ARFfamily structures in tomato and phylogenetic relationship between rice, potato, tomato, grape and Arabidopsis.
(A) The generic structures of Sl-ARF family except Sl-ARF6A. The gene size (kb) is indicated in the upper panel. The domain of Sl-ARF gene is indicated by different colours. The marker in Sl-ARF family showsSl-ARF2A, 2B, 3 and 4genes are spliced by TAS 3, Sl-ARF8A and 8B spliced by miRl67, and Sl-ARF10A, 10B, 16A, 16B and 17 spliced by miR160.(B) The unrooted tree was generated using MEGA4 program by neighbor-joining method. Bootstrap values (above 50%) from 1000 replicates are indicated at each branch. All Sl-ARFs contain a DBD (brown). Most of the Sl-ARF proteins except Sl-ARF3, 10, 24, 16 and 17 contain a carboxy-terminal domain related to the domains III and IV found in the Aux/IAA proteins (blue).Sl-ARF5, 6A, 7, 8A, 8B, 19 contains a middle region that corresponds to the predicted activation domain (green) found in some AtARFs. The remaining Sl-ARFs contains a predicted repression domain (red). Sl-ARF-6B and AtARF23 contain only a truncated DBD (B3 domain).