Figure 5.
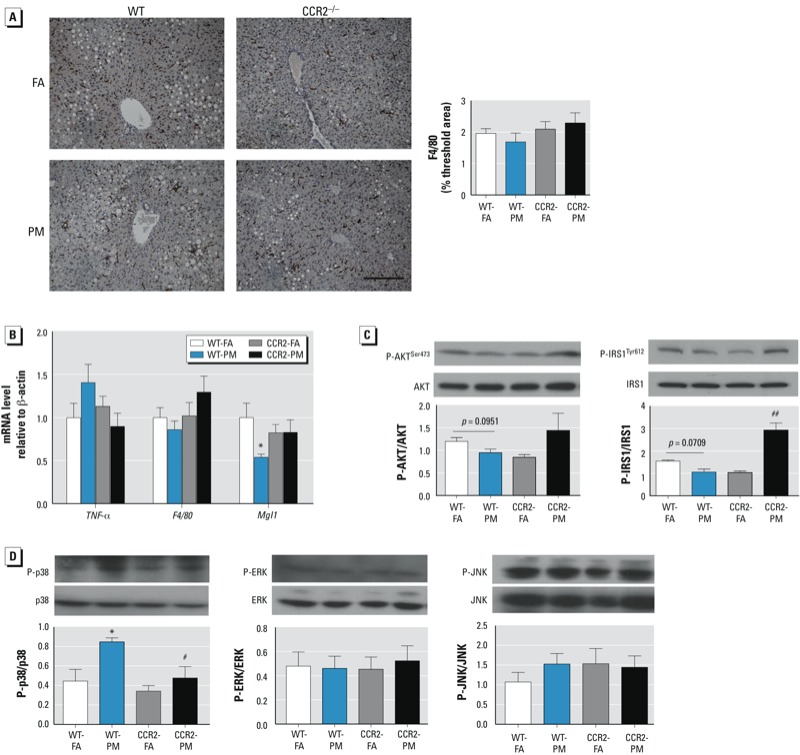
Effects of PM2.5 exposure and HFD on inflammation, insulin, and MAPK signaling pathways in the liver of WT and CCR2–/– mice; animals were exposed to PM2.5 or FA for 17 weeks. (A) Representative image (left; bar = 100 μm) and analysis (right) of F4/80 immunostaining (n = 7–9 mice/group). (B) mRNA levels of three genes involved in inflammation: F4/80, TNFα, and MgI1 (n = 7–9 mice/group). (C) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated AKT (P-AKT)/total AKT and phosphorylated IRS1 (P-IRS1)/total IRS1 (n = 3–7 mice/group). (D) Western blot analysis of signaling molecules involved in the MAPK pathway: phosphorylated p38/p38, phosphorylated ERK/ERK, and phosphorylated JNK/JNK(n = 3–5 mice/group). Data are presented as mean ± SE. *p < 0.05, compared with the WT‑FA group. #p < 0.05, and ##p < 0.01, compared with the WT‑PM group.
