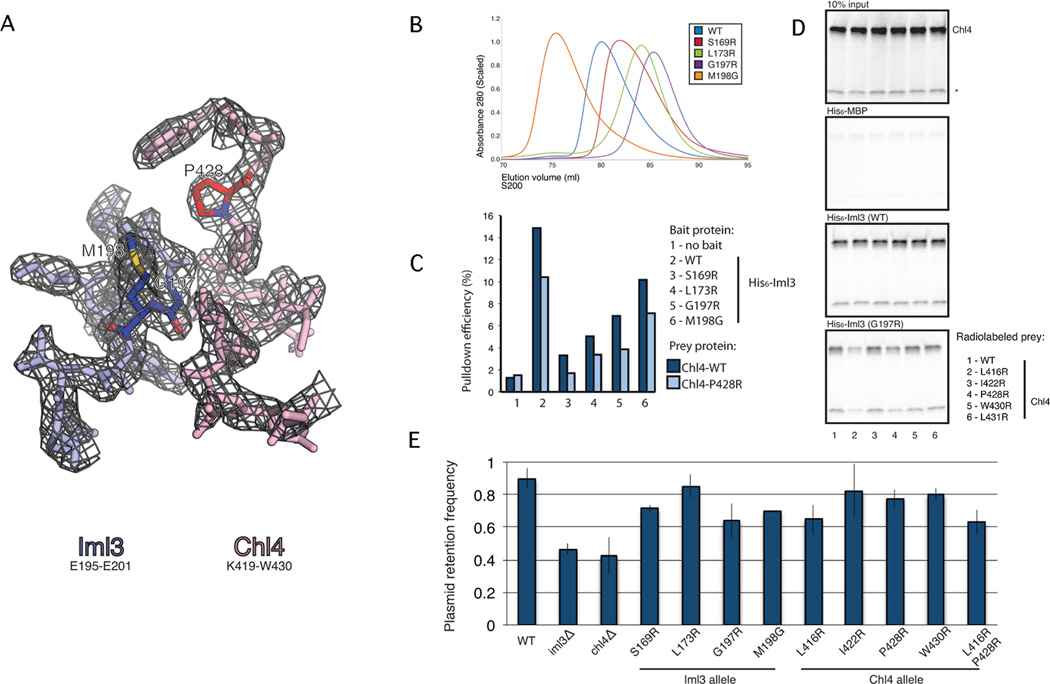
Figure 3. Point mutations that disrupt Iml3-Chl4 and Iml3-Iml3 interactions.
(A) Refined electron density at the Iml3-Chl4 dimer interface. 2Fo-Fc map contoured to 1.5σ for Iml3195–201 (blue) and Chl4419–430(red). Iml3G197, Iml3M198, and Chl4P428 are colored darker and by atom type. (B) Point mutations in the dimer interface impede Iml3 homodimerization (see also Figure S3). Iml3 proteins carrying His6 tags and the indicated point mutations were purified and subjected to size exclusion chromatography. The point mutations Iml3S169R, Iml3L173R, and Iml3G197R disrupt homodimer formation to varying degrees. Iml3M198G forms an Iml3 homodimer that is more stable than wild-type. (C) Iml3 point mutations in the dimer interface impede Iml3-Chl4 complex formation. Iml3 proteins carrying His6 tags and the indicated point mutations were purified and incubated with in vitro translated [35]S-labeled Chl4 or Chl4P428R. Ni2+-affinity pulldowns were performed, and bound protein was visualized by gel radiography. Integrated band intensities are plotted for the indicated pulldowns, and pulldown efficiency is given as the percent of input material recovered. All Iml3 point mutants disrupt Chl4 binding to varying degrees. Chl4P428R shows a mild defect in complex formation for all Iml3 proteins tested. (D) Chl4 point mutations that disrupt Iml3-Chl4 binding. [35]S-labeled Chl4 proteins (WT and five mutants) were translated as for (C), and Ni2+-affinity pulldowns were performed using His6-tagged Iml3 or His6-tagged Iml3G197R as bait. Chl4L416R and Chl4P428R disrupt binding to Iml3G197R. A non-specific band, presumably a truncation product of Chl4, is marked with a star. (E) Point mutations in the dimer interface partially recapitulate the plasmid missegregation phenotype seen in iml3- or chl4- strains. Haploid yeast strains carrying the indicated Iml3 or Chl4 alleles were tested for the ability to segregate a minichromosome absent auxotrophic selection. All point mutants tested except Iml3L173R showed plasmid segregation defects (three biological replicates, p-value < .05, Student’s t-test, error bars show +/− SD).