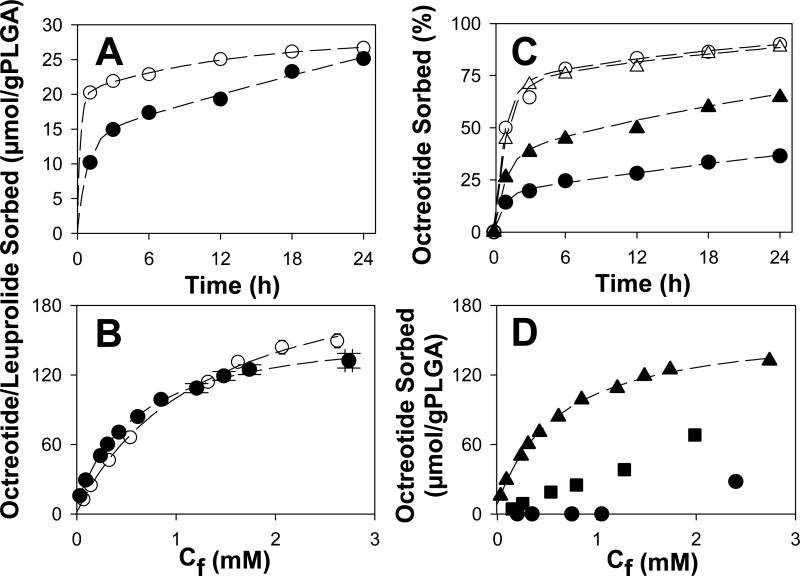
Fig. 1.
Characterization of peptide sorption to PLGA-COOH 50:50 at 37 °C. A) Effect of peptide type [leuprolide (○) vs. octreotide (●)] on sorption kinetics. B) 24-h sorption isotherm of leuprolide (○) and octreotide (●); Cf = final peptide concentration. C) Effect of ionic strength at pH 7 (0.1 M phosphate buffer (236 mM, ●), 0.1 M HEPES buffer (49 mM, ▲), 10 mM phosphate buffer (23 mM, ○) and 10 mM HEPES buffer (4 mM, Δ)) on the kinetics of octreotide sorption from 0.42 mM initial peptide concentration. D) Effect of pH (0.1 M HEPES buffer, pH 7.4 (▲), 0.1 M MES buffer, pH 5.5 (■), and 0.05 M DEPP buffer, pH 4.0 (●) on 24-h octreotide sorption isotherms. Sorption studies of A and B were conducted in 0.1 M HEPES buffer, pH 7. Initial peptide concentration was 0.4 mM in A and C and in the range of 0.2-4.0 mM in B and D. Symbols represent mean of 3 determinations. Dashed lines represent fits to a biexponential (A and C), and Langmuir models (B and D).