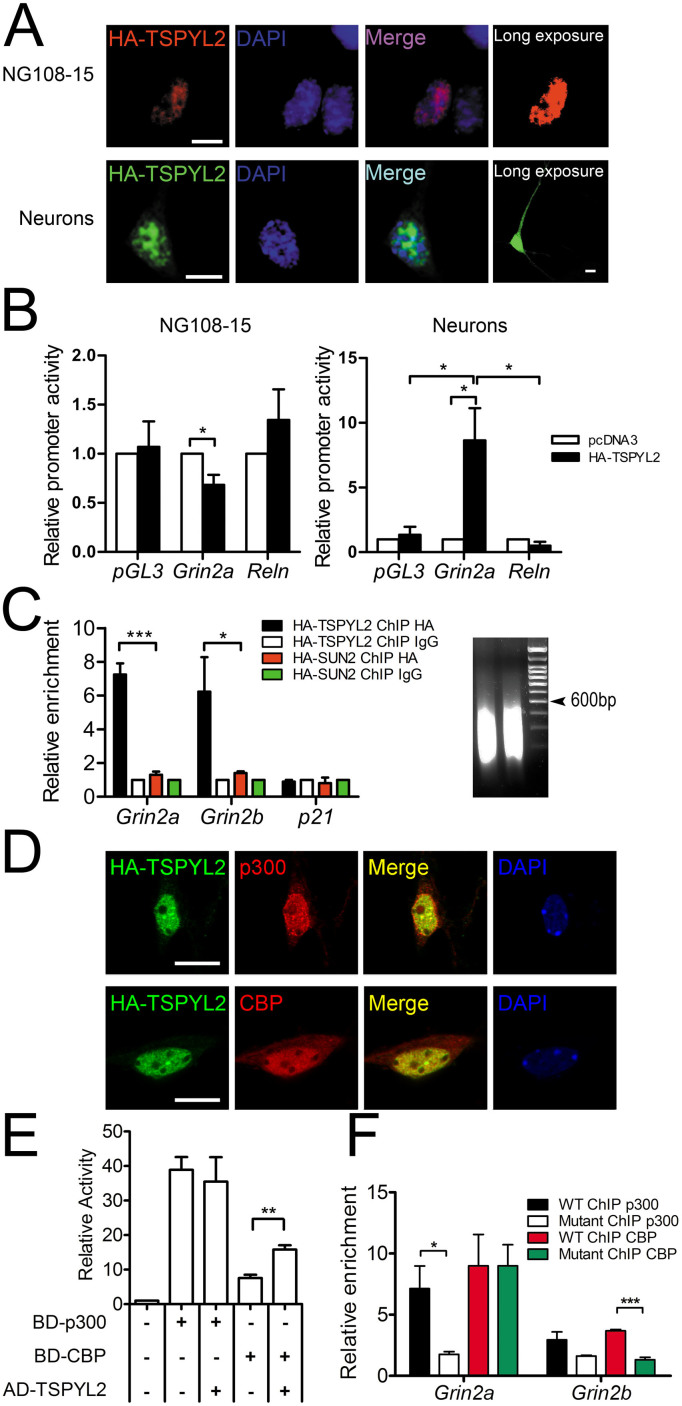
Figure 2. TSPYL2 activates the transcription of Grin2a and Grin2b.
(A), Immunocytochemistry of HA-tagged TSPYL2 in NG108-15 cells and primary hippocampal neurons. Exogenous TSPYL2 was localized in the nucleus. Low expression was observed in the cytoplasm in neurons. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B), Luciferase reporter assay of Grin2a promoter in NG108-15 cells and primary hippocampal neurons. Reln promoter served as a negative control. HA-TSPYL2 repressed the promoter activity of Grin2a in NG108-15 but activated it in hippocampal neurons (n = 3 independent experiments). (C), Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) of Grin2a and Grin2b promoters in transfected NG-108-15 cells. The signal was normalized to signal from input DNA and the ChIP IgG level was set as 1. Both promoters were pulled down by anti-HA antibody in HA-TSPYL2 transfected cells. p21 promoter was used as a negative control. HA-SUN2 transfected cells were used to show the specificity of HA-TSPYL2 binding (n = 3 independent transfections). The sizes of sonicated DNA fragments were concentrated between 200–600 bp (Right). (D), Co-localization between HA-TSPYL2 and endogenous p300 or CBP in primary hippocampal neurons by confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 10 μm. (E), Interaction between TSPYL2 and CBP in mammalian-two-hybrid assay. Primary hippocampal neurons were transfected with various plasmids with GAL4 DNA binding domain (BD) or VP16- activation domain (AD) (n = 3 independent experiments). (F), ChIP of Grin2a and Grin2b promoters in primary hippocampal neurons cultured for 14 days (n = 3 independent samples). Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student's t-test.