Fig. 15.
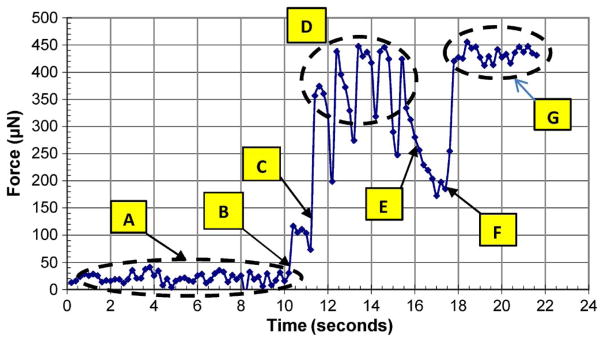
Measurement of actuation force for a MEMS microelectrode with chevron microactuators. (a) Microelectrode is moved toward the load cell’s surface. (b) Tip of microelectrode touched the load cell surface but did not make a good contact. (c) Microelectrode made a good contact and pushed the load cell. (d) Load cell senses the force generated by the thermal microactuator at the rate of 0.5 Hz. (e) Microactuator was turned off; the residual stress on the microelectrode due to the locking mechanism provided the resisting force. (f) Thermal actuator was turned back on and pushed the load cell. (g) Load cell sensed the force generated by the thermal microactuator at the rate of 1 Hz.
