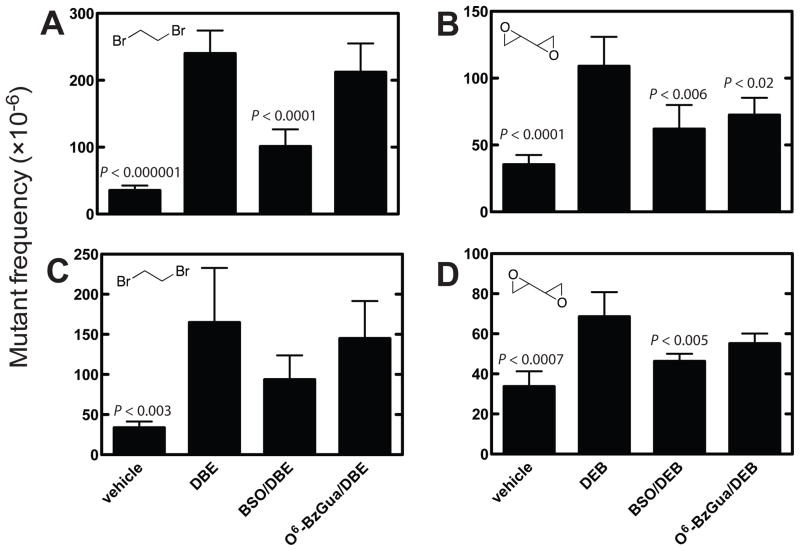
Figure 2.
cII mutant frequencies in liver of Big Blue® transgenic mice at 6 (A, B) and 24 h (C, D) after treatment with vehicle, dibromoethane (DBE), BSO/dibromoethane, or O6-BzGua/dibromoethane (A, C) and vehicle, DEB, BSO/DEB, or O6-BzGua/DEB (B, D). O6-BzGua (80 mg/kg, ip) was administered 1 h prior to treatment with dibromoethane (30 mg/kg, ip) or DEB (25 mg/kg, ip) and BSO (8 mg/kg, ip) was administered 2 h prior to treatment with dibromoethane (30 mg/kg, ip) or DEB (25 mg/kg, ip). The statistical significance values were from compareisons with the cII mutant frequencies induced by dibromoethane or DEB and evaluated using Student’s t-test (shown in figure). In Part A, the relative mutations frequencies (compared to the highest value, with dibromethane treatment set at 100%) were 15% for vehicle, 42% for +BSO, and 88% for +O6-BzGua. In Part B, the relative mutations frequencies (compared to the highest value, with dibromethane treatment set at 100%) were 20% for vehicle, 43% for +BSO, and 88% for +O6-BzGua. In Part C, the relative mutations frequencies (compared to the highest value, with DEB treatment set at 100%) were 32% for vehicle, 57% for +BSO, and 67% for +O6-BzGua. In Part D, the relative mutations frequencies (compared to the highest value, with DEB treatment set at 100%) were 49% for vehicle, 68% for +BSO, and 80% for +O6-BzGua.