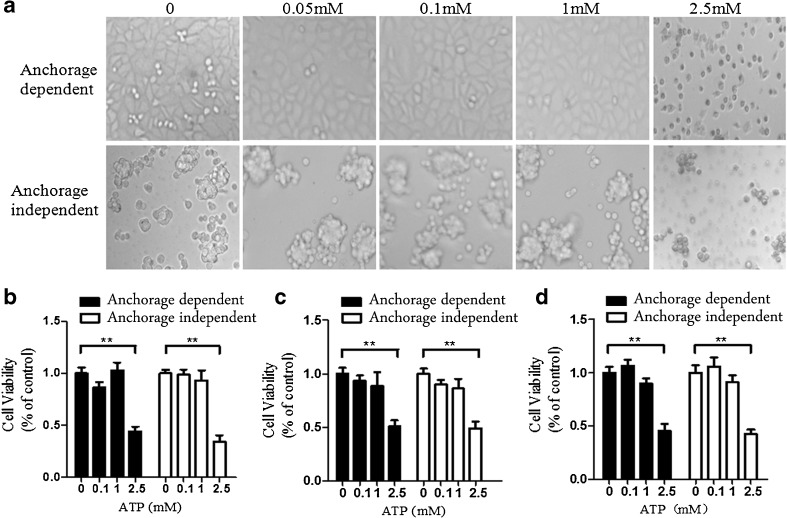
Fig. 1.
Cytotoxicity of eATP on anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent hepatoma cells. BEL7402, SMMC7721, and HepG2 hepatoma cells were plated into 96-well plates without or with poly-HEMA as anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent hepatoma models. a BEL7402 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of eATP (0–2.5 mM) and further cultured for another 24 h. Morphology changes were monitored and photographed for these models. b–d Anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent BEL7402 cells (b), SMMC7721 cells (c), and HepG2 cells (d) were treated with different concentrations of eATP for 24 h, and cell viabilities were detected by CCK-8 analysis. All figures presented are representative data from at least three independent triplicate experiments. **P < 0.01