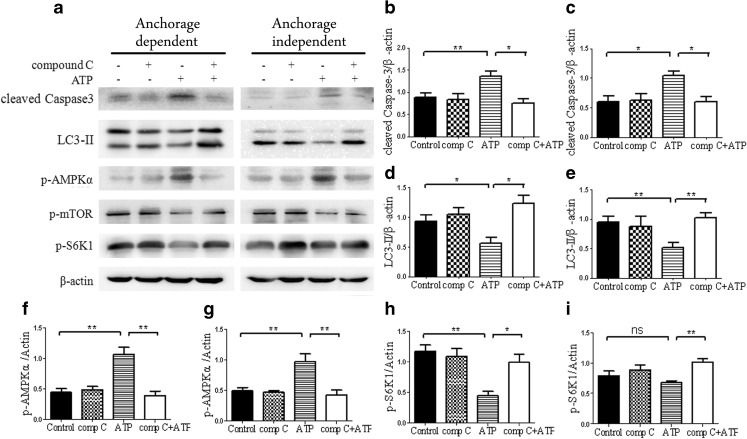
Fig. 9.
High dose of eATP-induced cytotoxicity was mediated through the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent BEL7402 cells were treated with 30 μM of compound C for 0.5 h and treated with 2.5 mM of eATP for 24 h. a–i Western blot analysis was performed (a), and densitometric analysis of bands was calculated using Image J software and normalized to β-actin (b, d, f and h for anchorage-dependent hepatoma cells and c, e, g and i for anchorage-independent cells). Presented figures are representative data from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01