Fig 2.
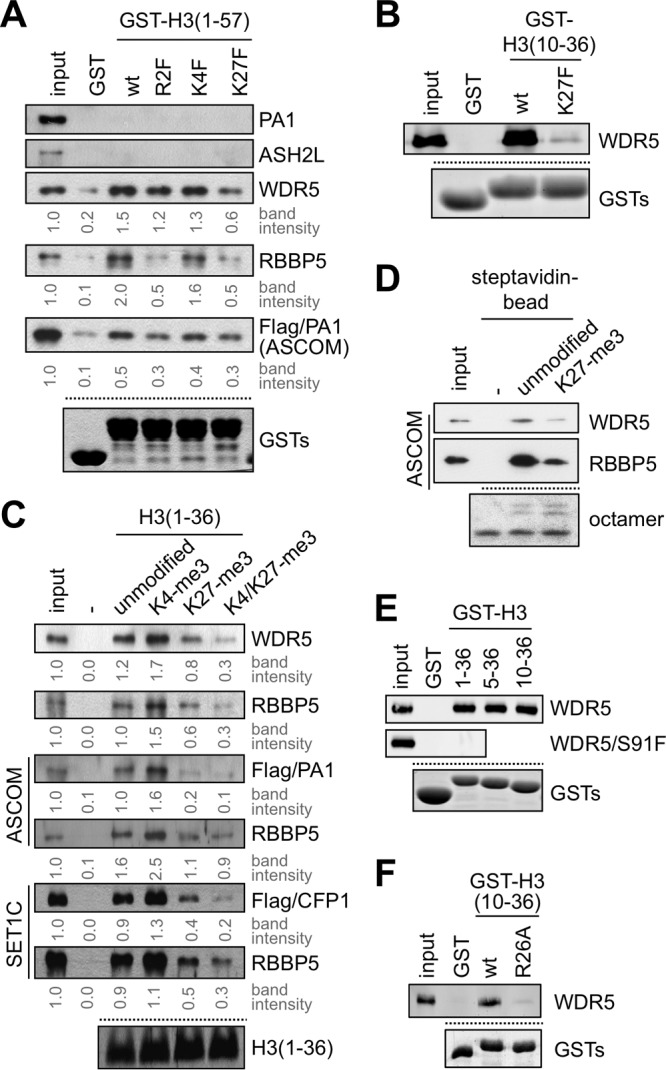
H3K27 trimethylation impairs the interaction of H3 and WDR5/RBBP5. (A, B, E, and F) GST pulldown assay with GST fusions to indicated H3 fragments and either in vitro translated Flag-PA1, Flag-ASH2L, Flag-WDR5, Flag-WDR5/S91F, or Flag-RBBP5 or purified ASCOM complex with Flag-tagged PA1. PA1, ASH2L, WDR5, RBBP5, and ASCOM were detected by immunoblotting with anti-Flag antibody. Coomassie blue staining of GST fusions is shown as a loading control. (C) Immobilized peptide pulldown assay using indicated H3 peptides either with in vitro translated Flag-WDR5 or Flag-RBBP5 or with purified ASCOM (via Flag-PA1 or RBBP5) or purified SET1 complex (via Flag-CFP1 or RBBP5). WDR5, RBBP5, PA1, and CFP1 were detected by immunoblotting with anti-Flag or RBBP5 antibody. Coomassie blue staining of H3 peptides is shown as a loading control. (D) Binding assays of ASCOM (monitored by anti-WDR5 and anti-RBBP5 immunoblotting) to immobilized reconstituted mononucleosomes containing either unmodified or K27 trimethylated H3. Coomassie blue staining of octamers in mononucleosomes is shown as a loading control. Similar results were also obtained with the SET1 complex (data not shown). Input in panel D is 10%, and all other inputs are 5%. wt, wild type.
