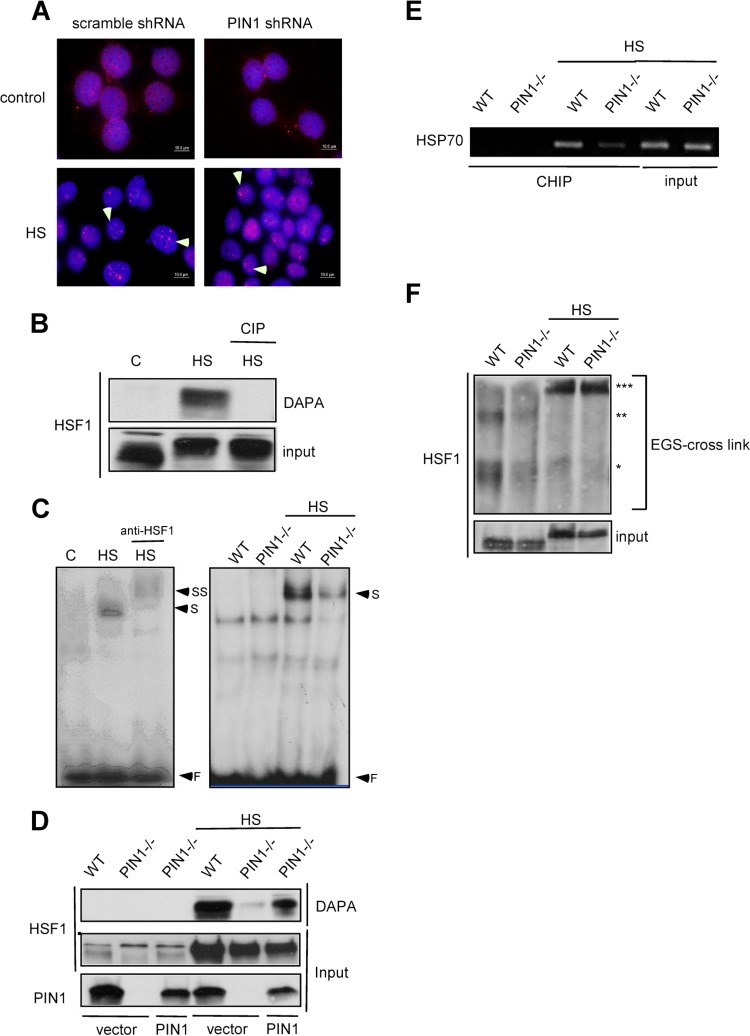
Fig 2.
PIN1 is required for HSF1 DNA-binding activity. (A) MCF7 cells were infected by scrambled-shRNA or PIN1-shRNA lentivirus constructs. HSF1 was detected by immunofluorescence in control or heat shock-treated MCF7 control shRNA-treated and PIN1-shRNA-treated cells. (B) To determine the DNA-binding activity levels, cell lysates were treated with calf alkaline phosphatase (CIP) prior to DNA-affinity precipitation assay (DAPA) and immunoblotting for HSF1. (C) (Left) Supershift analysis shows that the induced DNA-protein complexes contain HSF1. (Right) EMSA analysis of whole-cell extracts from wild-type and PIN1−/− MEF cells treated with 43°C heat shock. (D) The PIN1−/− MEF cells were transfected with mouse PIN1 DNA. The nuclear extracts of wild type, PIN1−/− MEFs and PIN1-expressing PIN1−/− MEFs were incubated with the probe and immunoblotted for HSF1. (E) In vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of HSF1-DNA-binding activity in wild-type and PIN1−/− MEF cells treated with 43°C heat shock. (F) Total protein extracts of MEFs were evaluated for HSF1 multimerization by EGS cross-linking, SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotting with an HSF1-specific antibody. *, **, and *** on the right indicate the expected migration of the HSF1 monomer, dimer, and trimer, respectively.