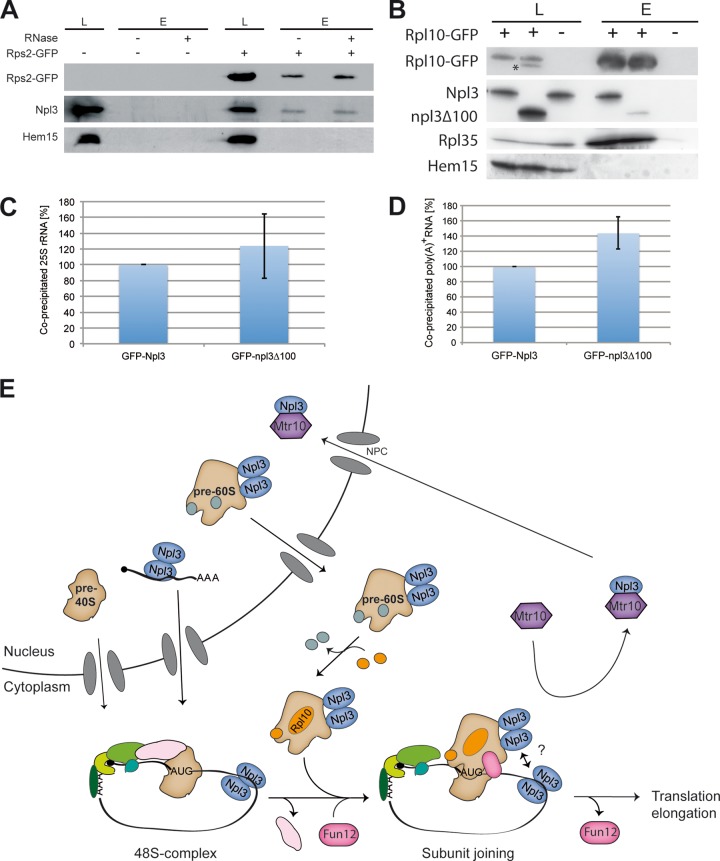
Fig 6.
Full-length Npl3 forms a complex with Rpl10. (A) Npl3 physically interacts with the small ribosomal subunit. Coimmunoprecipitations were performed with Rps2-GFP and Npl3. The results are shown in a Western blot. Hem15 served as a negative control. (B) The binding of npl3Δ100 to Rpl10 is disturbed. RNase was added to all samples. Western blots of coimmunoprecipitations of Rpl10-GFP with Npl3, npl3Δ100, Rpl35, and the negative control protein Hem15 were performed. The asterisk marks the npl3Δ100 protein from a previous detection. L, lysate; E, eluate. (C) The dimerization domain of Npl3 is not essential for 25S rRNA binding. RNA coimmunoprecipitations were performed with GFP-tagged Npl3 or npl3Δ100. The coprecipitated 25S rRNA was detected by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Binding of npl3Δ100 to the rRNA was quantified in three different experiments relative to the wild-type protein. (D) The dimerization domain of Npl3 is not essential for mRNA binding. RNA coimmunoprecipitations were performed with GFP-tagged Npl3 or npl3Δ100. The coprecipitated poly(A)+ RNA was detected by dot blot hybridization with a 32P-labeled oligo(dT) probe and set into relation to the immunoprecipitated protein amount. The mRNA binding of GFP-npl3Δ100 was compared in three different experiments to the wild type. (E) Model for the novel function of Npl3 in translation initiation. Npl3 mediates the nuclear export of mRNA. In the cytoplasm the initiation complex assembles on the mRNA and, upon scanning and AUG recognition, the 40S ribosomal subunit waits for the joining of the mature 60S ribosomal subunit. In addition, Npl3 mediates the export of pre-60S particles and stays bound to the subunit during cytoplasmic maturation. The mature Rpl10-containing 60S subunit joins the 48S initiation complex, which is supported by Fun12 and dimerized Npl3, possibly by its multimerization with the mRNA-bound counterparts. eIF5B/Fun12 dissociates from the complex and allows translation elongation. Finally, the import receptor Mtr10 dissociates Npl3 and recycles it back to the nucleus for other rounds of transport.