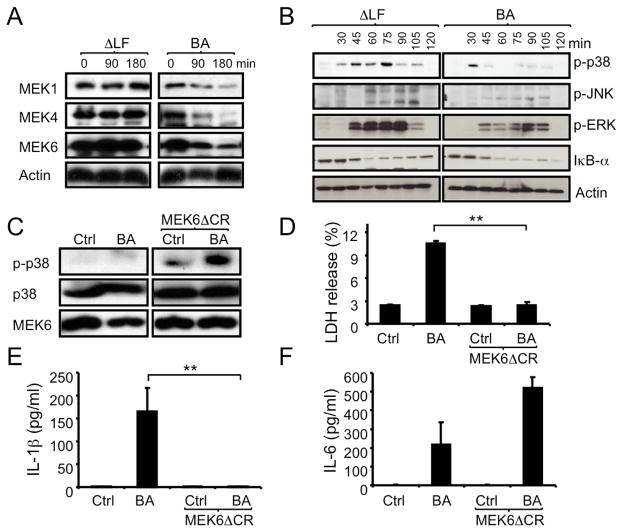
Figure 2. B. anthracis-induced inflammasome activation depends on LF and inhibition of p38.
(A,B) C57BL/6 macrophages were infected with WT (BA) or ΔLF B. anthracis. At the indicated times, cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting of 2 separate gels of the same experiment for MEK proteolysis (A) and MAPK phosphorylation (B).
(C,D) RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with MEK6ΔCR or an empty vector. Transfected cells were left uninfected or infected with B. anthracis and 1 hr later cell lysates were prepared and analyzed for p38 phosphorylation by immunoblotting (C). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release to the culture supernatant was measured after 4 hr of infection (D). Results are means ± SD, **p < 0.01 denote significant differences between the groups.
(E,F) RAW264.7 cells were transfected and infected as above. After 8 hr, IL-1β (E) and IL-6 (F) in culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. Results are means ± SD, **p < 0.01 denote significant differences between the groups. All experiments were repeated at least 3 times and the results of one representative experiment are shown.