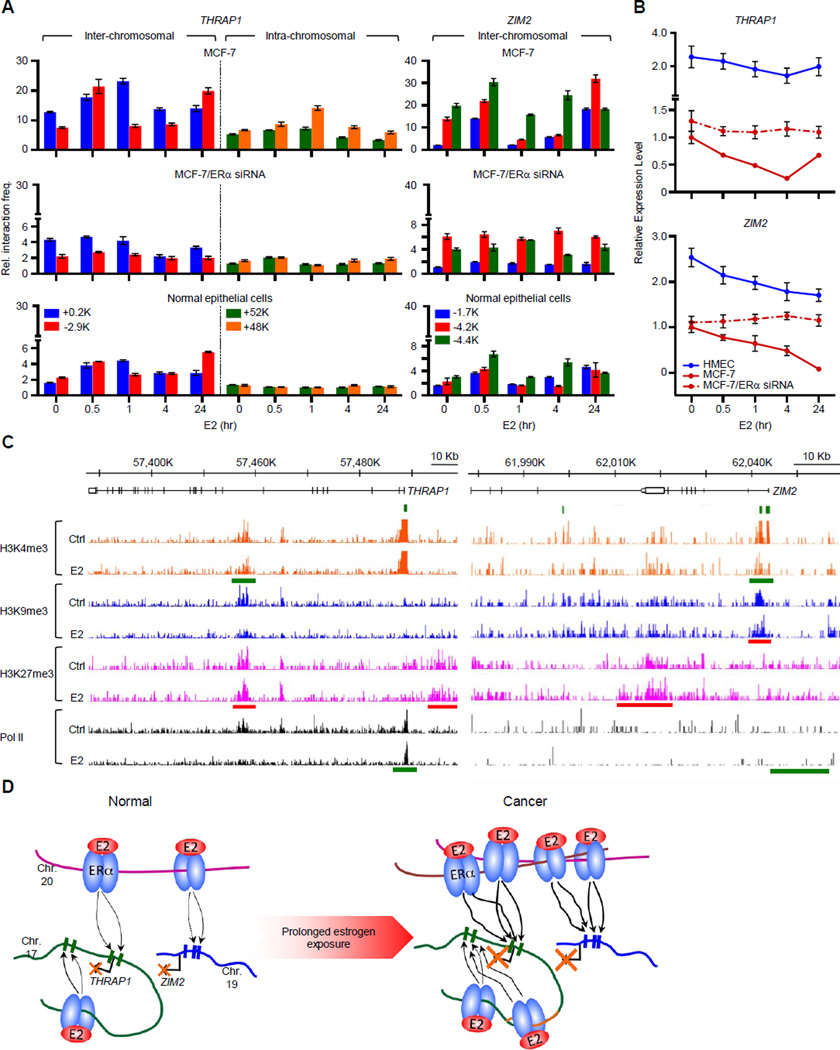
Figure 6. Two Representative Examples of Amplified DERE-regulated Target Genes through Long-range Chromatin Interactions.
(A) Chromosome conformation capture coupled with quantitative PCR (3C-qPCR) analysis of two target loci, ZIM2 and THRAP1. Cross-linked chromatin from E2-treated MCF-7 and normal epithelial cells was digested with either BamHI or HindIII and then ligated under diluted conditions. DEREs at 20q13 were designated as “baits”, and digested areas of two candidate loci, ZIM2 and THRAP1, were “interrogated fragments”. Ligated DNA was subjected to the 3C-qPCR. Data are shown as relative interaction frequencies compared to those of GAPDH as an internal control. Mean ± SD (n=6).
(B) Expression analyses of THRAP1 and ZIM2 in normal breast epithelial cells (HMEC) or cancer cells (MCF-7) in response to E2 (70 nM) determining using quantitative RT-PCR. Cells with or without ESR1 (ERα) knockdown by siRNA were treated with E2 for the indicated times. See also Figure S5 for the effect of siRNA on ESR1 expression.
(C) Genomic landscapes of histone modifications and Pol II occupancy on THRAP1 and ZIM2 loci upon estrogen stimulation. A published ChIP-seq data including three histone marks (H3K4me3, H3K9me3, and H3K27me3) and Pol II was used to investigate the occupancy of epigenetic marks on the two genes from −20-Kb upstream region of transcription start sites to transcription termination sites (Joseph et al., 2010). Red bars, increased occupancy; green bars, reduced occupancy.
(D) Proposed coordinate model of DERE-modulated chromatin interactions for transcriptional regulation in response to estrogen. In normal cells, DEREs at 20q13 are brought to THRAP1 (at 17q23.2) and ZIM2 (at 19q13.43), respectively, through chromatin movement to repress expression. During tumor progression under continuous estrogen exposure, genomic fusions and amplifications occur in the 20q13 DEREs attributed to prolonged physical contact between DEREs in an unstable cancer genome. The DEREs from 20q13 are replicated and inserted into different chromosomes, leading to increased interaction frequencies between DEREs and the respective gene loci, which profoundly alter their transcriptional regulation.