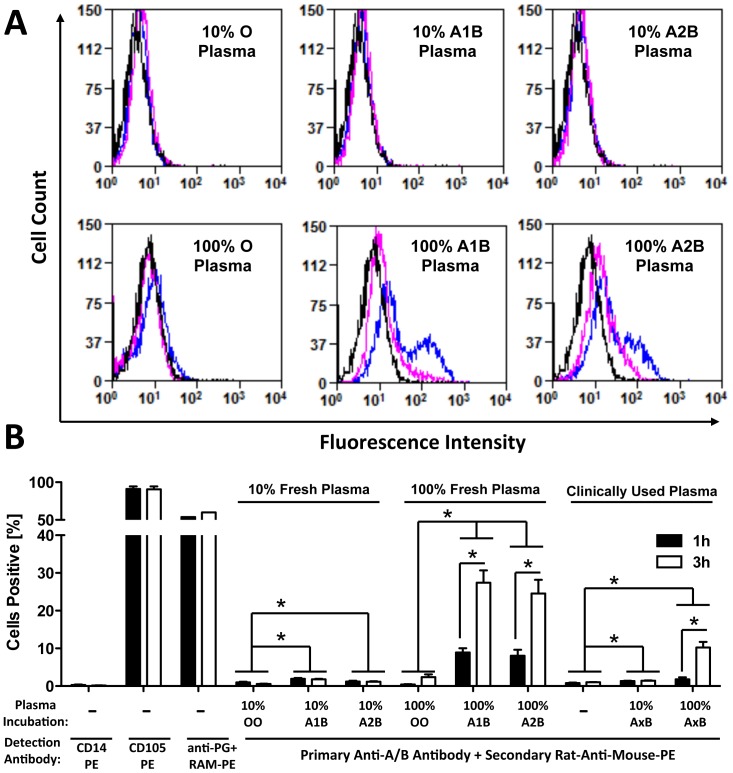
Figure 3. Adsorption of ABO antigens to MSCs from human AB plasma.
MSCs are often washed and reconstituted in human AB plasma when prepared for systemic infusion. We therefore used flow cytometry, in order to detect potential binding of A/B-antigens to freshly thawed blood type O MSCs (n = 4) after incubation with human plasmas of different blood types (n = 3 each). (A) Histogram overlay for detection of soluble A/B-antigen binding from plasma to MSCs after a 1-hour (pink curve) or 3-hour (blue curve) incubation with 10% or 100% O, A1B, A2B, or clinical A1/2B plasma of unknown A1 or A2 subtype. Upon incubation, cells were washed with serum free media, to remove non-bound plasma components, and A/B-antigen binding was detected with primary mouse-anti-human A/B antibody, followed by incubation with secondary rat-anti-mouse-PE antibody (RAM-PE), and compared to binding of secondary antibody only to untreated cells (black curves). (B) Cells detected positive (%) after two different plasma adsorption times (1 vs. 3 hours). Five AB plasmas of unknowns A subtype, which were previously used for clinical MSC infusion (A1/2 B), were compared to O, A1B and A2B plasma. As controls, cells were labeled with CD14-PE (negative labeling control), CD105-PE (positive control), and anti-paragloboside (PG) + RAM-PE (secondary antibody labeling control), or anti-A/B + RAM-PE, to detect A/B-antigen binding, as indicated below the figure. Mean±SD, * P < 0.05.