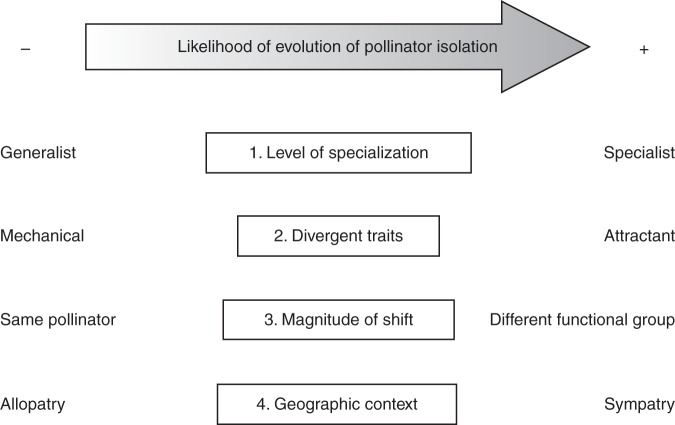
Fig. 4.
Four axes along which shifts in pollination system can vary. Axis 1 represents the degree of pollinator specialization, varying from generalist through functionally specialized (e.g. only bees), to extreme specialist. Axis 2 represents the type and extent of trait divergence, varying from divergence in mechanical traits to variation in attractant traits. Axis 3 represents the magnitude of pollination system shifts, varying from divergent use of the same pollinator through minor shifts between similar pollinator species to major shifts among functional pollinator groups (e.g. bees to birds). Axis 4 represents the geographic context of pollination system shift, varying from allopatric, through parapatric to sympatric ecotype ranges. The evolution of pollinator isolation is more likely for shifts in pollination system characterized by the intrinsic and extrinsic conditions listed on the right of each axis compared to those listed on the left.