Fig. 4.
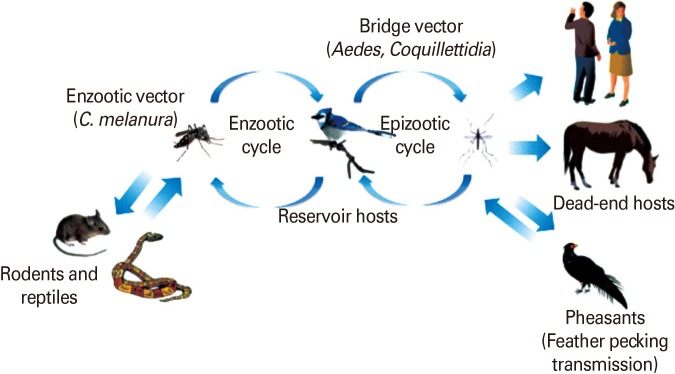
Enzootic and epizootic/epidemic transmission cycles of Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV). The enzootic EEEV transmission cycle is maintained between passerine birds as reservoir/amplification hosts and Culiseta melanura, as the main enzootic vector in swamp habitats. Rodents/marsupials may serve as principal enzootic vectors and reservoirs in South America. Passerine birds develop extremely high levels of viremia, enough to infect both enzootic vectors as well as a variety of bridge vectors. Humans and equids are dead-end hosts since they do not develop sufficient viremia to transmit the virus.