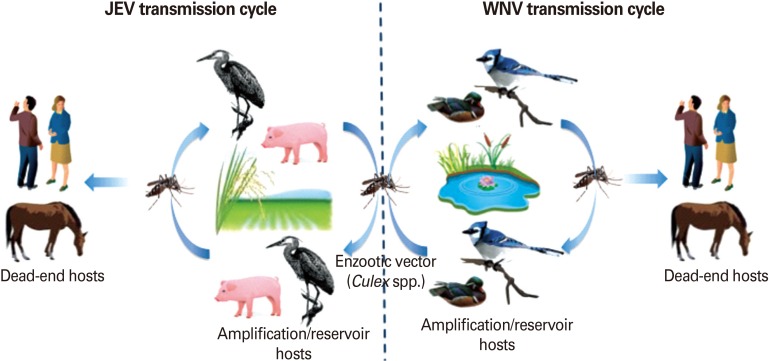
Fig. 7.
Enzootic and epizootic/epidemic transmission cycles of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and West Nile virus (WNV). Left: JEV is transmitted by primarily Culex tritaeniorhynchus. Pigs and aquatic birds are the efficient amplification and reservoir hosts of JEV that develop high-titered viremia. Humans and horses are dead-end hosts since the level of viremia is insufficient for mosquito transmission. Right: WNV maintains an enzootic transmission cycle between Culex mosquitoes and birds (reservoir host). Horses, humans, and other mammals infected in a spillover transmission are "dead-end" hosts.