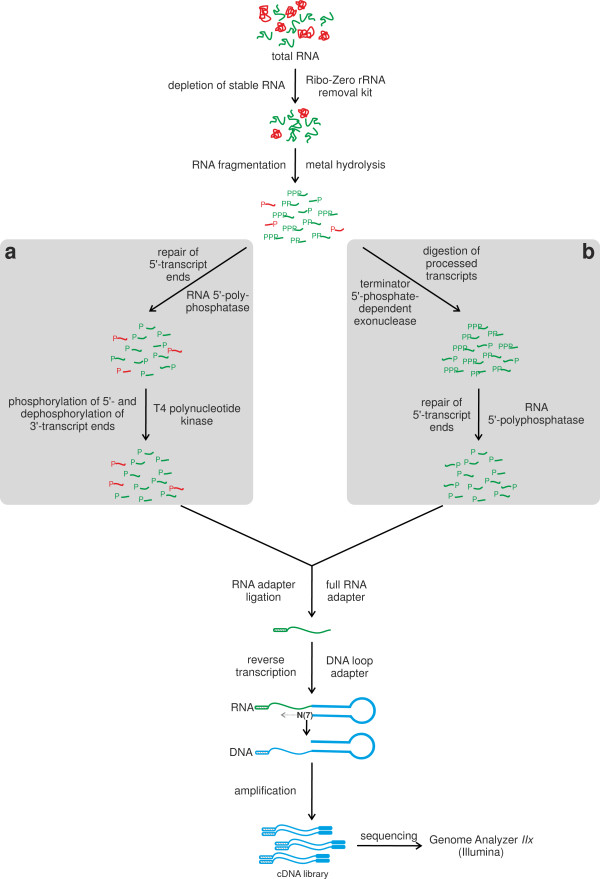
Figure 1.
Experimental workflow for the preparation of a whole transcriptome library (a) and of a library enriched for primary 5′-transcript ends (b). Both protocols start with isolated total RNA. Stable RNA is then depleted using the Ribo-Zero rRNA removal kit and the obtained RNA is fragmented my metal hydrolysis to a size of 200 - 500 nt. For the whole transcriptome library (a) the 5′-triphosphate ends are processed to 5′-monophosphate ends by a RNA 5′-polyphosphatase, unphosphorylated 5′-ends are phosphorylated, and phosphorylated 3′-ends are then dephosphorylated using T4 polynucleotide kinase. For the native 5′-end protocol (b), all fragments containing a 5′-monophosphate are degraded by treatment with a 5′-phosphate dependent exonuclease and the 5′-triphosphate ends of native transcripts are then processed to 5′-monophosphate ends by a RNA 5′-polyphosphatase. Next, for both libraries RNA adapters are ligated to the 5′-ends carrying a 5′-monophosphate group. The tagging of the 3′-end of the RNA with flanking sequences necessary for reverse transcription is performed in a ligation-free approach with a loop DNA adapter containing seven unpaired wobble bases at its 3′-end. After reverse transcription of the RNA fragments into cDNA fragments, the cDNA fragments are amplified, tagged with sequencing linkers at their ends by PCR and finally sequenced. Stable RNA species (rRNA, tRNA) are depicted in red, other RNAs are given in green, and DNA in blue.