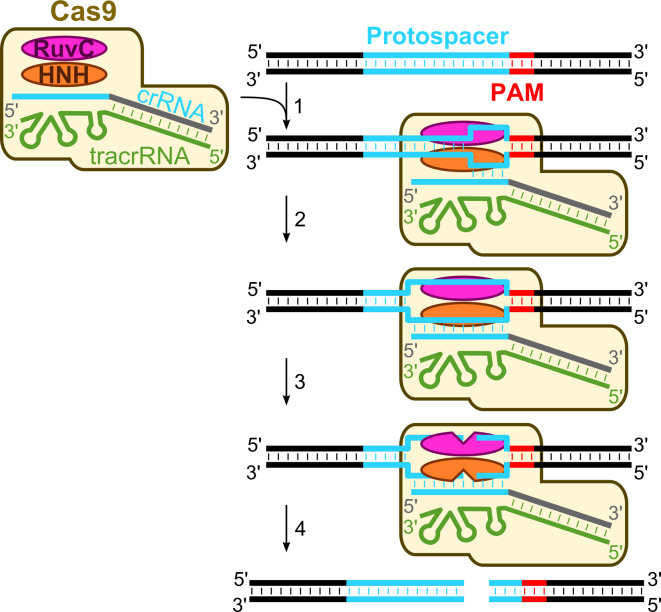
Fig. 3.
DNA-interference in the Type II CRISPR–Cas systems. The Cas9–crRNA–tracrRNA ternary complex scans DNA for a protospacer sequence and PAM. Once the correct PAM and a short primary hybridization sequence (“seed”) are identified (1), the crRNA basepairs with a complementary DNA strand forming R-loop (2). Once the R-loop is formed, Cas9 cuts both target and non-target DNA strands using the RuvC and the HNH active sites, respectively (3). Cleavage occurs 3 nt before PAM, yielding blunt-end DNA products (4)