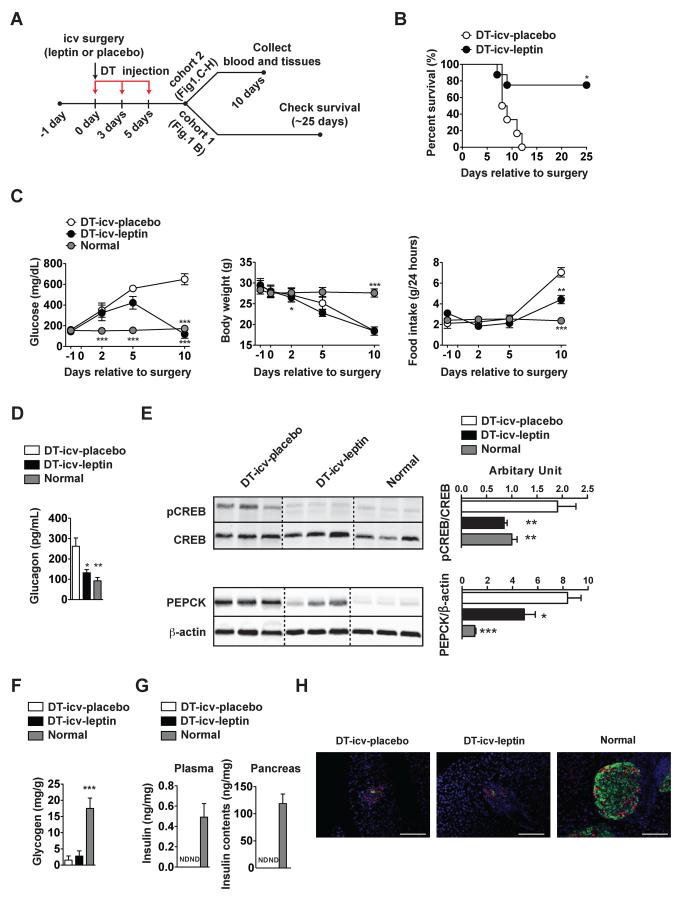
Figure 1. icv leptin administration reverses lethality and improves hyperglycemia caused by complete insulin deficiency.
(A) Experimental design using RIP-DTR mice (Thorel et al., 2010). Leptin (25 ng/hour) or placebo (phosphate-buffered saline; PBS) was intracerebroventricularly (icv) administered starting at day 0 in DT-icv-leptin or DT-icv-placebo mice, respectively. DT-icv-leptin and DT-icv-placebo mice were rendered insulin deficient by intraperitoneal (ip) diphtheria toxin (DT) administration at day 0, 3, and 5. Age-matched, non-diabetic controls were used to gather parameters in surgically- and DT-untreated normal mice (normal group). (B) Kaplan-Meier survival analyses were performed on DT-icv-leptin and DT-icv-placebo mice; Statistical analyses were done using by Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon Test. ***P<0.001 versus DT-icv-placebo mice (numbers of mice at day 0 of DT-icv-leptin and DT-icv-placebo were 8 and 6, respectively). (C) Glucose levels in the blood, body weight, food intake, (D) glucagon in the plasma, (E) hepatic protein levels of pCREB and PEPCK, (F) glycogen in the liver, (G) insulin levels in the plasma and whole pancreas and (H) representative distribution of cells expressing insulin (green) and glucagon (red) in the pancreas of DT-icv-placebo, DT-icv-leptin and normal mice. Statistical analyses were done using one-way ANOVA (Tukey's Multiple Comparison Test). Values are mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4–6). ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05 versus DT-icv-placebo mice. ND = below the threshold of detection. Scale bar size = 100 μm. See also Figure S1