Fig. 2.
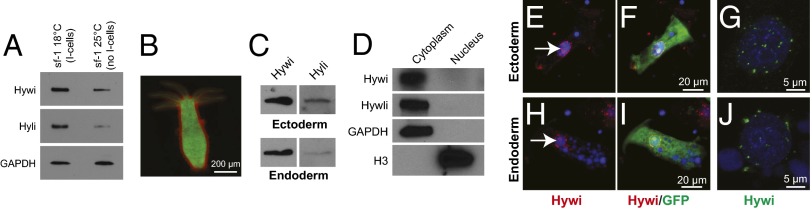
PIWI proteins are cytoplasmic and expressed in the mitotically active somatic epithelial cells. (A) Expression of Hywi and Hyli protein is detected by immunoblot in epithelialized mutant strain (sf-1) Hydra, which lose the interstitial lineage when cultured at 25 °C (46, 47). (B) To test for epithelial expression of Hywi and Hyli, ectodermal cells expressing DsRed2 and endodermal cells expressing GFP were isolated by FACS (SI Appendix, Fig. S4) and subjected to immunoblot analysis with Hywi and Hyli antibodies. (C) Hywi and Hyli were detected in both the ectodermal and endodermal epithelial cells. (D) To test the subcellular localization of Hywi and Hyli, nuclear (histone H3) and cytoplasmic (GAPDH) fractions were probed with the Hywi and Hyli antibodies; both proteins were detected selectively in the cytoplasmic fractions. To determine the subcellular localization of Hywi in epithelial cells, staining was performed on transgenic Hydra that express GFP in either the ectodermal (E–G) or endodermal (H–J) epithelial cells. (E–J) Hywi accumulates in perinuclear granules (arrows in E and H) in ectodermal (E–G) and endodermal (H–J) epithelial cells. (G and J) Hywi-positive granules are detected around the nucleus of epithelial cells in confocal Z-stack projections. (E–J) DNA is labeled with Hoechst 33342; vacuoles in endodermal cells (H and I) are also Hoechst-positive.
