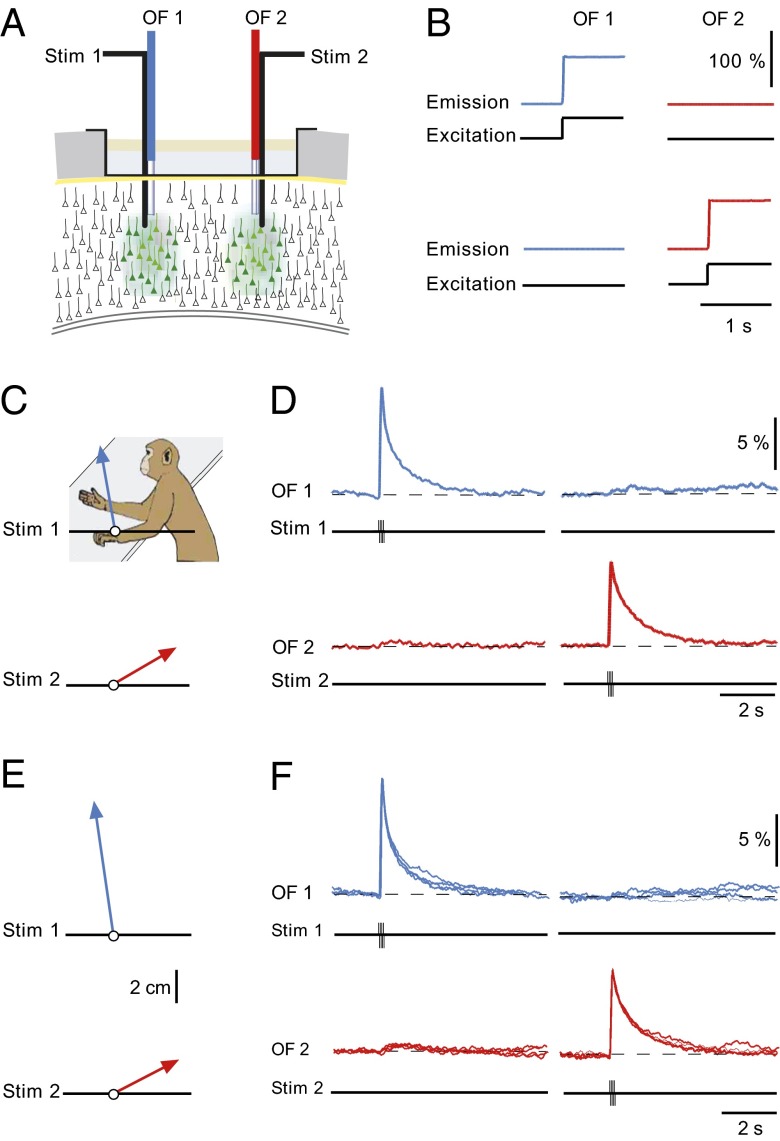
Fig. 3.
Ca2+ signals restricted to local cortical domains determine specific movements. (A) Scheme of the experimental arrangement for applying current pulses and recording Ca2+ signals simultaneously from two distinct locations of the primary motor cortex. (B, Upper) Delivery of stimulation light through optical fiber 1 (OF1, 488 nm, black trace), produced Ca2+ dye-dependent fluorescence signal (blue), but no response was detected by optical fiber 2 (OF2, red). (Lower) Opposite result when stimulation through OF2. (C) Distinct arm movements produced by microstimulation at two sites (Stim1 and Stim2) in M1. Stim1: burst of eight pulses at 100 Hz, 25 µA; Stim 2: burst of eight pulses at 100 Hz, 30 µA. The image indicates the resting position of the arm. (D) The local Ca2+ signals corresponding to the movements shown in C. (E and F) The average movement vectors (n = 4) and the corresponding superposition of four consecutive local domain Ca2+ signals, as in C and D, respectively.