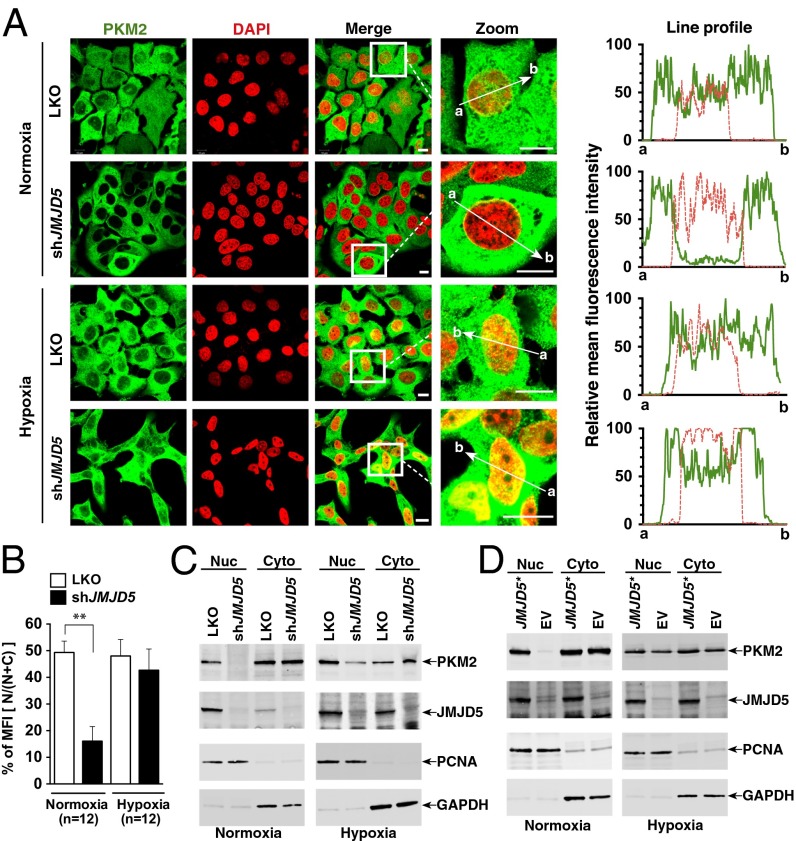
Fig. 3.
JMJD5 regulates the nuclear translocation of PKM2. (A) Subcellular localization of PKM2 in MCF-7 cells. Cells were immunostained with anti-PKM2 (PKM2, green). The nucleus is marked with DAPI (red). Merged images (Merge) are shown. The framed regions are zoomed in the fourth row (Zoom). The line profiles of PKM2 and DAPI signals were measured by ZEN 2011 (Carl Zeiss) software. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (B) Analysis of the mean fluorescence intensity of PKM2 in the cytosol and nucleus. Mean values from 12 independent cells from three preparations were determined by the ZEN 2011 Histogram program. The relative fluorescence intensity in the nucleus is expressed as percentage of MFI [N/(N + C)]. Statistical significance was evaluated using the paired Student t test. (C) Nuclear and cytosolic lysates were prepared from LKO and MCF-7–shJMJD5 cells exposed to normoxia or hypoxia, followed by immunoblotting analysis. (D) Subcellular localization of JMJD5 and PKM2 in shJMJD5 cells introduced with the shRNA-resistant JMJD5 (JMJD5*) or empty vector (EV). Cyto, cytoplasm; Nuc, nucleus; PCNA, proliferating-cell nuclear antigen; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.