Figure 1.
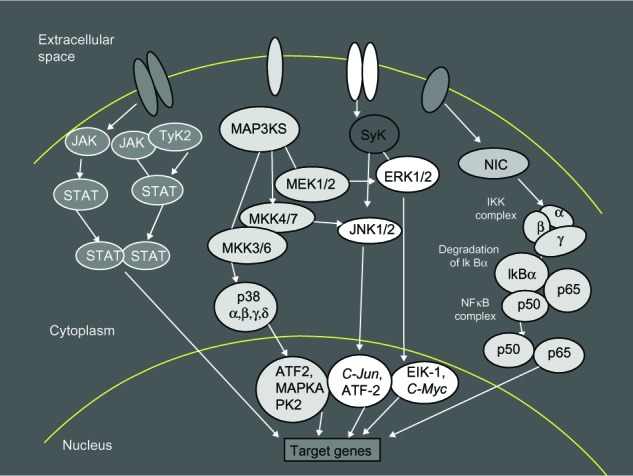
Intracellular signaling pathways.
Notes: Intracellular pathways offer many options for the inhibition of cytokine signaling. JAK/STAT pathways are one of several intracellular hubs in the inflammatory cytokine network. There are several kinase cascades operating for the intracellular signaling; these include: JAK, MAP, Syk, NF-κB, STAT, TyK2, ERK, MAP3KS that phosphorylates and activates a MKK (for example, ERK), JNK, C-Jun, ATF2, Elk-1, C-Myc, NIK, IKK, and IκBα.
Abbreviations: JAK, C-Jun N-terminal kinase; TyK2, tyrosine kinase 2; MAP3KS, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; MeK 1/2, dual-specificity kinase MAP kinase kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; NIC, nuclear factor-kappa B inducing kinase; MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; IKK, inhibitor kappa B kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IkBα, subunits of IKK; ATF2, activating transcription factor 2; MAPKA, mitogen-activated protein kinase A; PK2, protein kinase 2; C-Jun, transcription factor C-Jun; Elk-1, Ets-like protein 1 transcription factor; C-Myc, cellular oncogene; NIK, nuclear factor kappa B inducer kinase.
