Fig. 4.
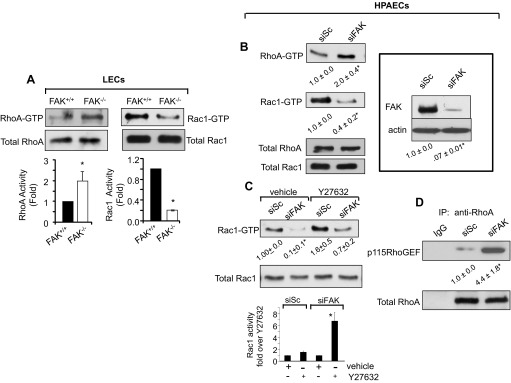
FAK deletion impairs normal balance between RhoA and Rac1 activities. A and B: effect of FAK deletion on RhoA and Rac1 activities. FAK−/− and FAK+/+ LECs were lysed, and the activity of RhoA or Rac1 was determined using rhotekin or PAK pull down beads (A). Data represent means ± SD of GTPase activities compared with those in FAK+/+ LECs. *Significant difference from FAK+/+ LECs (P < 0.05; n = 3). Human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs) transfected with scrambled (siSc) or FAK (siFAK) small-interfering RNA (siRNA) were lysed to determine RhoA and Rac1 activities (B). In parallel, lysates were immunoblotted with anti-FAK and anti-actin Abs to assess FAK depletion in ECs using actin as a loading control (inset). Blot is representative of findings from three individual experiments. *Significant difference from siSc-transfected HPAECs (P < 0.05; n = 3). C: RhoA inhibits Rac1 activity. Scrambled and FAK siRNA-expressing HPAECs were incubated with 10 μM Y-27632 to inhibit Rho kinase (ROCK), a downstream effector of RhoA. After 30 min, cells were lysed, and Rac1 activity was determined to assess whether inhibition of ROCK restores normal Rac1 activity. *Significant difference from siSc-transfected HPAECs (P < 0.05; n = 3). In bar graph, Rac1 activity in Y-27632-pretreated siSc- or siFAK-transfected cells is plotted relative to their respective vehicle-treated values to better discern the level of restoration seen in siFAK cells after inhibiting ROCK. *Significant difference from siSc-transfected HPAECs or vehicle-treated siFAK cells (P < 0.05; n = 3). D: FAK depletion promotes RhoA interaction with p115RhoGEF. Lysates from scrambled and FAK siRNA-expressing HPAECs were immunoprecipitated with either control IgG or anti-RhoA antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-p115RhoGEF and anti-RhoA Abs. The blot shown is representative of data from multiple experiments. *Significant difference from siSc-transfected HPAECs (P < 0.05; n = 4).
