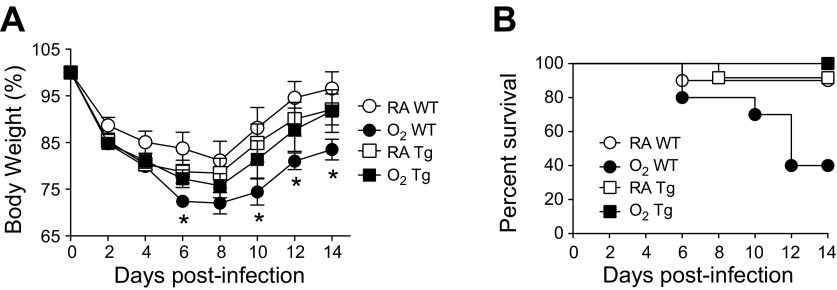
Fig. 2.
EC-SOD reduces morbidity and enhances survival of infected adult mice exposed to hyperoxia at birth. Adult female WT and EC-SOD Tg mice exposed to RA or O2 at birth were intranasally infected with a sublethal dose of influenza A virus. Body weight (A) and survival (B) were monitored for 14 days following influenza A virus infection, and results are shown as %body weight and %survival, respectively (n = 8–12 mice/group). Analysis of differences between mean body weights over time was first determined by a one-way analysis of variance (P < 0.05), followed by an unpaired t-test (*P < 0.05 when compared with RA WT). Analysis of differences in survival over time was determined by a Mantel-Cox test (P < 0.05).