Fig. 1.
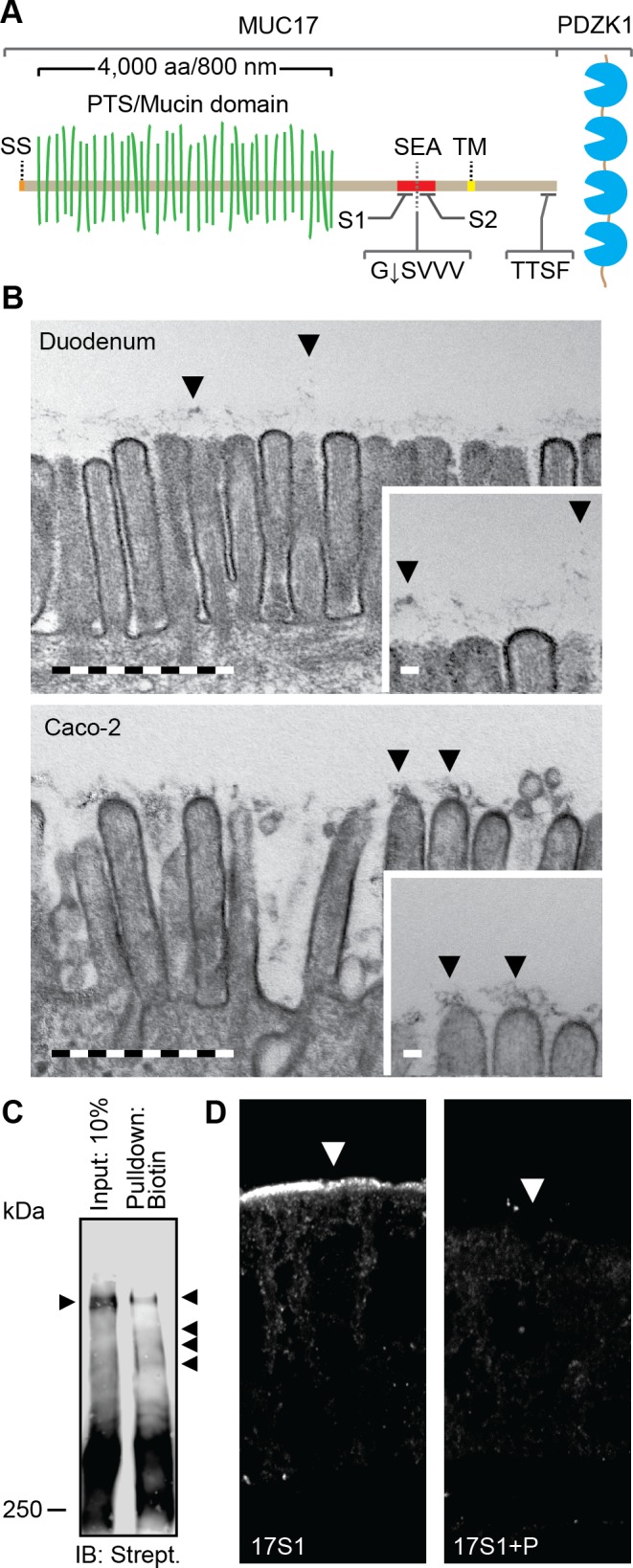
The transmembrane mucin MUC17 is a component of the glycocalyx covering apical membranes of Caco-2 cells. A: schematic view of the domain organization of MUC17. SS, signal sequence; PTS, proline-, threonine-, and serine-rich region called the mucin domain when O-glycosylated; SEA, SEA domain; TM, transmembrane domain. G↓SVVV represents the consensus sequence of the native SEA cleavage site. S1 and S2 indicate the position of epitopes recognized by anti-MUC17S1 and anti-MUC17S2 pAbs. TTSF represents the class I PDZ binding motif that allows binding to the scaffolding protein PDZK1. B: transmission electron microscopy of microvilli distributed on the apical surface of human duodenal enterocytes (top) and polarized Caco-2 cells (bottom). Insets: magnifications of the larger micrographs. Arrows point at the glycocalyx. Bars in large micrographs = 1 μm. Bars in insets = 100 nm. C: expression of surface glycoproteins on apical surface of Caco-2 cells assessed by surface biotinylation using biotin hydrazide. Biotinylated high-molecular glycoproteins were detected using streptavidin HRP. Arrows indicate separated biotinylated glycoproteins. IB, immunoblot. D: staining of MUC17 on apical surface of polarized Caco-2 cells (left). The specificity of anti-MUC17S1 pAb against MUC17 was assessed by neutralizing the antibody with its corresponding immunizing peptide (P) (right). Arrows point towards the apical plasma membrane.
