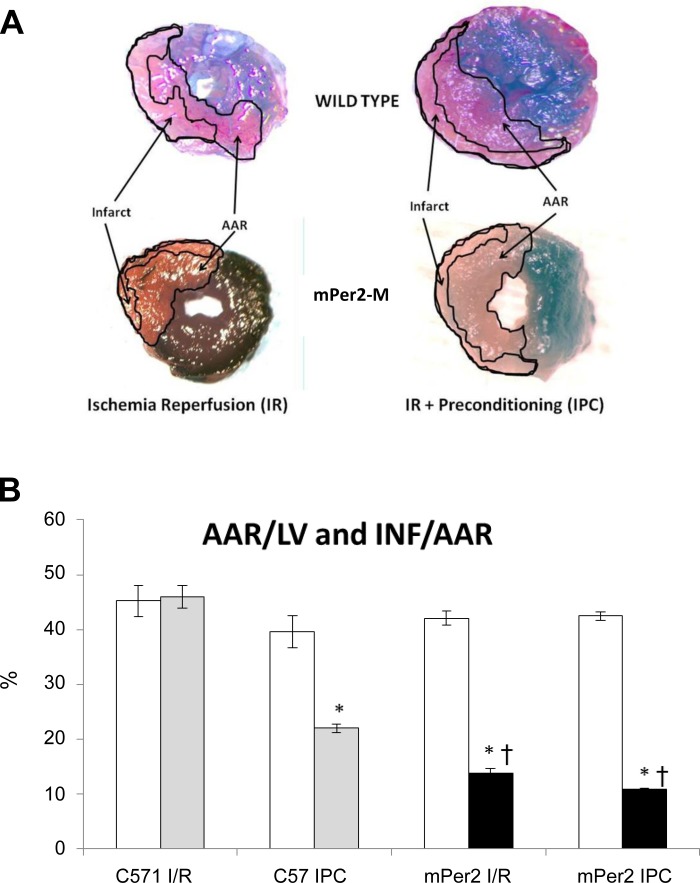
Fig. 1.
Evan's blue- and 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC)-stained hearts and morphometric measures of area at risk (AAR)/left ventricle (LV) and infarct area (INF)/AAR. The images in A are representative images of Evan's blue- and TTC-stained hearts from each of the four experimental groups (×20). The graph in B shows the AAR as a function of the LV (white bars) and the INF as a function of the AAR (gray and black bars). There were no differences in AAR/LV between the 4 experimental groups. As expected, ischemic preconditioning (IPC) in WT C57 mouse hearts reduced the INF/AAR by 52% (*P < 0.001). The INF/AAR in mPer2-M hearts in both the ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) and IPC groups was reduced by 67 and 74%, respectively (*P < 0.001), and both groups were significantly less than the C57 IPC group (†P < 0.001). There was no difference in INF/AAR between the mPer I/R and IPC groups.