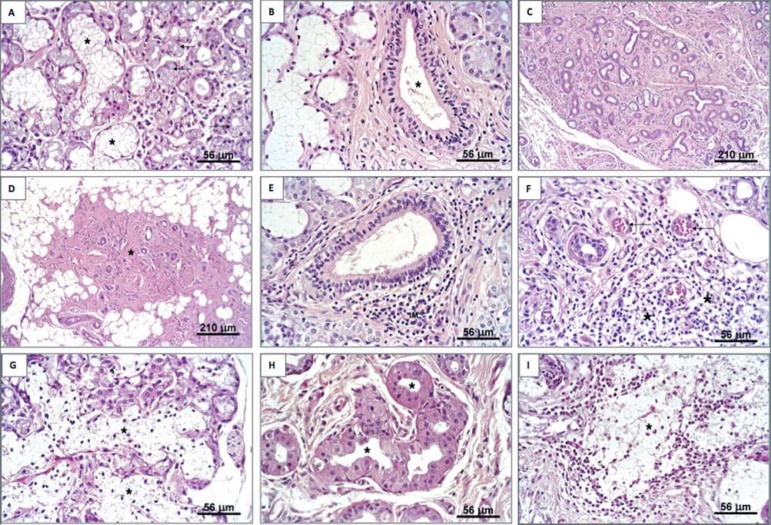
Figure 2.
Sublingual glands of cadavers and MFERSG patients (hematoxylin & eosin staining). a: Normal lobule (*) and atrophic acini (arrows). b: True duct (excretory interlobular). c: Intense acinar atrophy, presence of duct-like structures and intense substitution of the parenchyma by fibrous tissue. d: intense replacement with fibrous and adipose tissue containing a few traces of parenchyma (*). e: Periductal focal mononuclear infiltrate (IM). f: Diffuse mononuclear infiltrate (*) and congested blood vessels. g: Acinar autolysis (*). h: Oncocytosis (*) in ductal cells. i: Mucous extravasation (*) MFERSG=mouth floor enlargements related to the sublingual glands