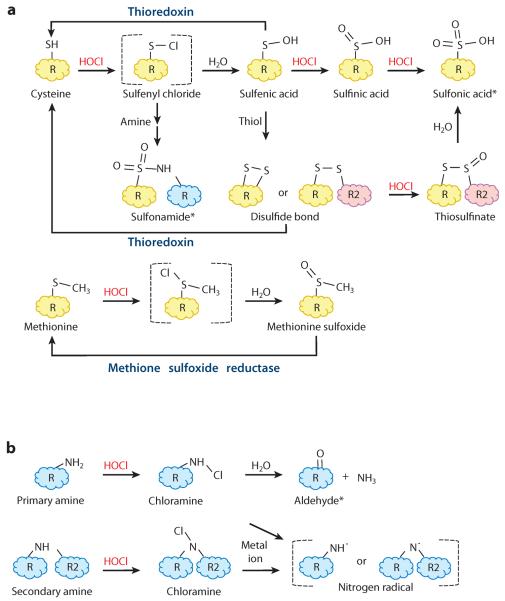
Figure 1.
Reactions of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) with biomolecules. Reaction of HOCl with (a) sulfur-containing compounds or (b) amines. Brackets indicate unstable reactive intermediates. Enzymes known to repair oxidized cysteine or methionine residues in bacteria are indicated. Asterisks indicate irreversibly oxidized dead-end products.