Figure 2.
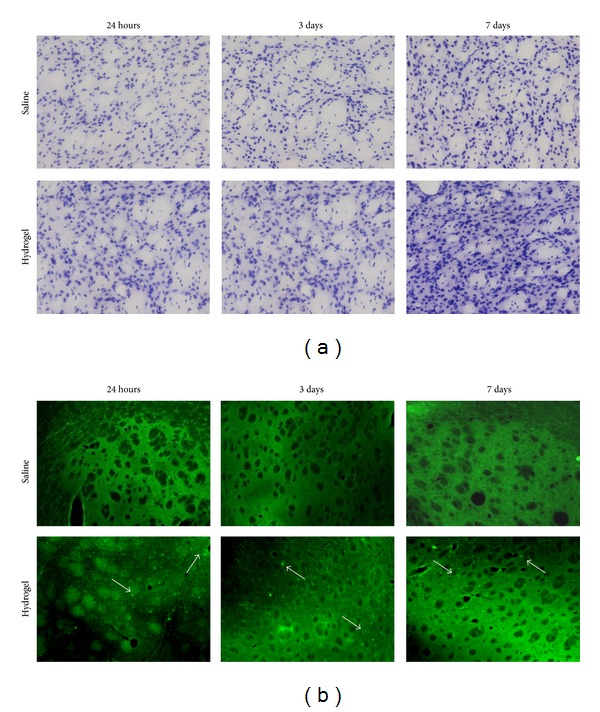
Evaluation of the biocompatibility of an injectable hydrogel formulation for brain applications. We designed and prepared in saline (0.9% NaCl) a hydrogel (pH 7.2) composed of Carbomer 974P (4.3% w/v), PEG (Mw = 600 g mol−1, 12.2% v/v), and glycerol (14.6% v/v). An aliquot (2 μL) was diluted 1 : 1 (v/v) with saline to simulate the cell loading and stereotaxically injected into the mouse striatum, keeping the contralateral brain hemisphere as a control. (a) Nissl staining to point out brain tissue cytoarchitecture. In the hydrogel-injected hemisphere, tissue hypertrophy was present after 7 days. (b) Fluoro-Jade A staining. This staining allows tracking cell damage points that appear as bright green dots. Differently from the control, where few dots were visible, in the hydrogel-injected hemisphere neuronal and glial damage was detectable as early as 24 h after injection. The white arrows point to the Fluoro-Jade A positive points.
