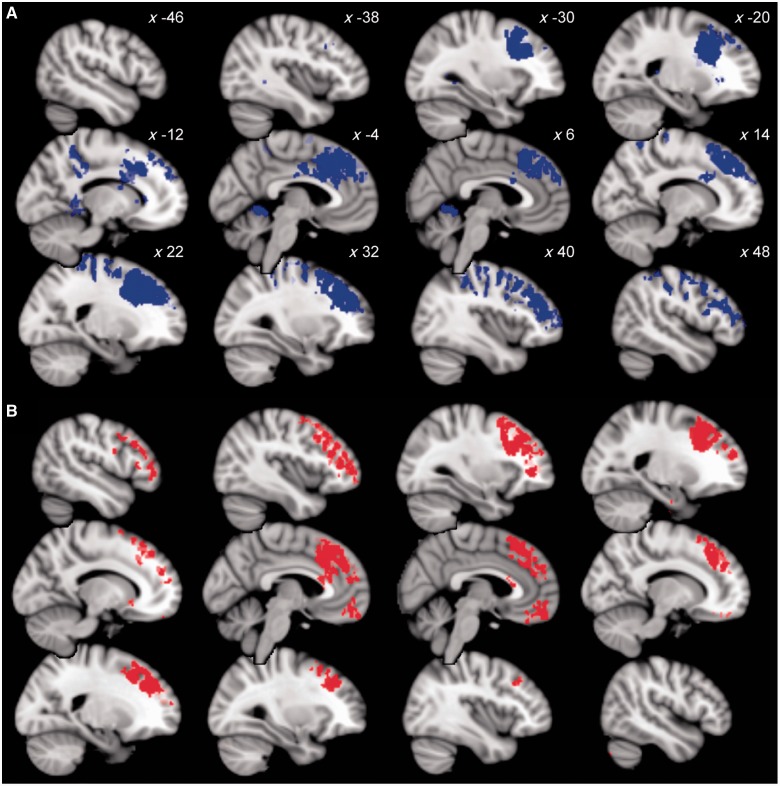
Figure 5.
Functional connectivity of the pre-SMA associated with abnormal action binding. (A) Areas showing increased functional connectivity with the pre-SMA at rest in patients, relative to control subjects (blue; P < 0.05, FWE corrected). Slice x-coordinate is indicated. A large fronto-parietal network showed increased coactivation with the pre-SMA, including the cerebellum, intraparietal sulcus, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex and lateral prefrontal cortex. (B) Voxels showing positive correlation between coactivation with the pre-SMA and action binding measures in patients (red; P < 0.05, FWE corrected). Slices as in A. These correlations indicate a predominantly frontal cortical network associated with agency and the disorders of voluntary action, including alien limb phenomena and apraxia.