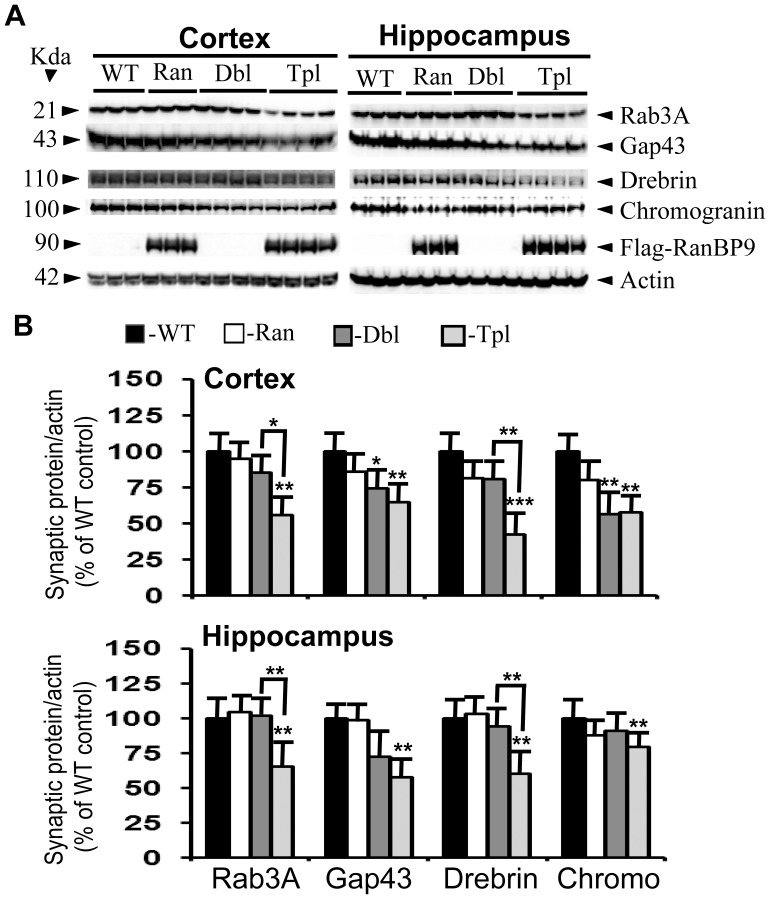
Figure 4. RanBP9 overexpression exacerbates reduction of synaptic protein levels at 6-months of age in the cortex and the hippocampus of APΔE9 mice.
A: Brain homogenates were processed and synaptic proteins, flag-tagged RanBP9 and actin were detected as in legend to figure 1. B: ImageJ quantitation and normalization to actin levels revealed significant differences. Rab3A levels were further reduced by 30% and 36% in the cortex and hippocampus respectively in the triple transgenic mice compared to double transgenic mice. Similarly, drebrin levels were further reduced by 38% and 33% in the cortex and the hippocampus in the triple transgenic mice compared to double transgenic mice. Gap43 levels were reduced in the cortex by 36% in the triple transgenic mice and by 26% in the double transgenic mice compared to WT controls. In the hippocampus gap43 levels were reduced only in the triple transgenic mice by 43%. In the cortex, chromogranin levels were reduced by 44% in the double and by 44% in the triple transgenic mice, whereas in the hippocampus a 21% reduction was observed only in the triple transgenic mice. ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test revealed significant differences. *, p<0.05, **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001 in APΔE9/RanBP9 or APΔE9 mice compared to WT mice as indicated in the figure. The data are mean±SEM, n = 6 for WT and RanBP9 mice, and n = 8 for APΔE9 and APΔE9/RanBP9 genotypes.