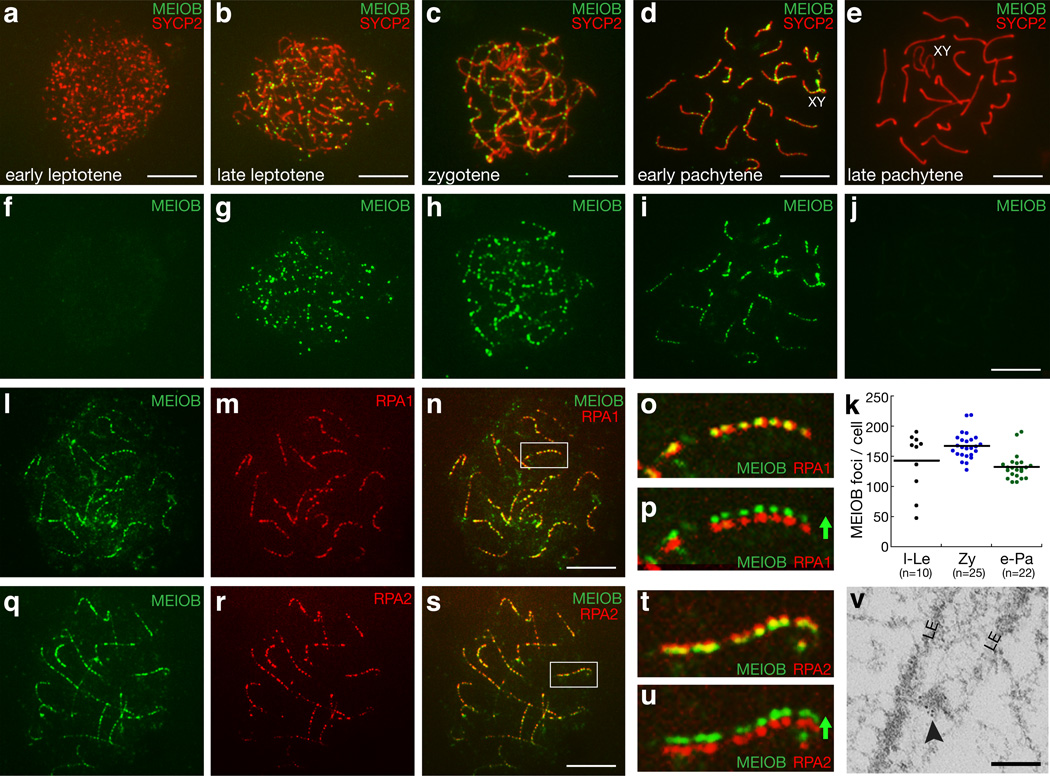
Figure 2. MEIOB colocalizes with RPA in foci on meiotic chromosomes.
(a–e) Distribution pattern of MEIOB foci on chromatin of spermatocytes from early leptotene through late pachytene stages. (f–j) the same cells in panels a–e are shown with MEIOB labeling only. (k) Number of MEIOB foci in spermatocytes at successive stages of meiotic prophase I. Stages were determined by SYCP2 staining. l-Le, late leptotene; Zy, zygotene; e-Pa, early pachytene; n indicates the number of cells counted. The line indicates the average. (l–p) MEIOB colocalizes with RPA1 on the meiotic chromosomes of spermatocytes. The same spermatocyte is shown with MEIOB labeling only (l), RPA1 labeling only (m), and in a merged image (n). Enlarged views of the marked chromosome in panel n are shown in panels o and p (without or with offset channels). (q–u) MEIOB colocalizes with RPA2 on the meiotic chromosomes of spermatocytes. The same spermatocyte is shown with MEIOB labeling only (q), RPA2 labeling only (r), and in a merged image (s). Enlarged views of the marked chromosome in panel s are shown in panels t and u (without or with offset channels). (v) Electron microscopy with immunogold (6 nm particles, arrowhead) -labeled MEIOB reveals signal between the lateral elements (LE) in spermatocytes. Scale bars: a–s, 10 µm; v, 0.2 µm.