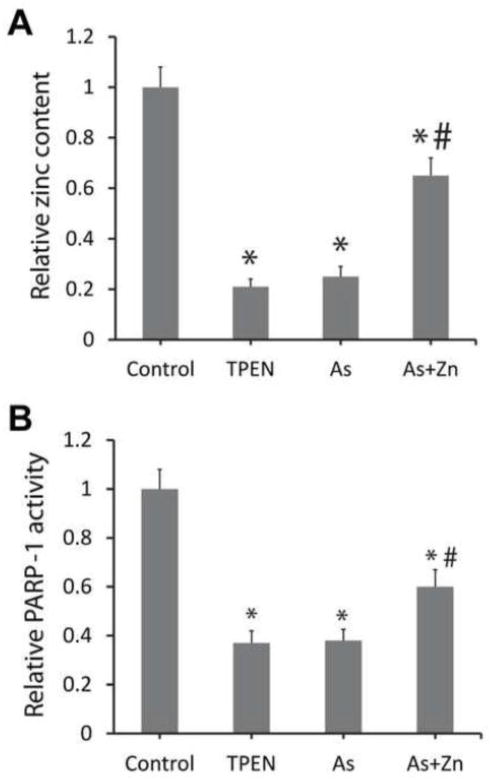
Fig 2.
Arsenite and TPEN induced loss of zinc content and activity in PARP-1 protein. HaCat cells were treated with 5 μM TPEN, 2 μM arsenite, or 2 μM arsenite + 2 μM zinc for 24 hours. After treatment, the cells were collected and PARP-1 was isolated by immunoprecipitation from the cell extracts. (A) 10 mM H2O2 were incubated with the isolated PARP-1 to release the zinc. Released zinc was determined by measuring the absorbance at 492 nm after the addition of 50 μM PAR. The data were presented as the zinc content of treatment group divided by that of the control and expressed as the means±SD from three experiments. (B) The activity of PARP-1 in the cell extracts was detected by immunochemical detection of poly(ADP-ribose). The relative activity was indicated as the activity of treatment group divided by that of the control and presented as the means±SD from three experiments. *, p < 0.01 vs. Control; #, p<0.01 vs. arsenic alone.