Figure 3.
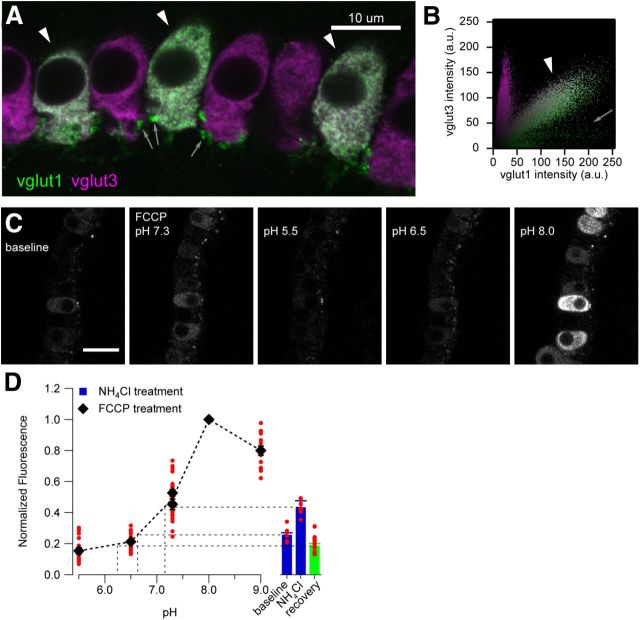
Expression and basic characterization of vglut1–pHluorin in IHCs. A, Subcellular localization of vglut1–pHluorin highly resembles that of the endogenous vesicular glutamate transporter vglut3. Single confocal section of immunolabeled IHCs showing expression pattern of vglut1–pHluorin (labeled with anti-vglut1 antibody, green) and vglut3 (magenta). Arrowheads indicate coexpression of vglut1 and vglut3 in IHCs; arrows indicate vglut1-positive postsynaptic boutons. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Correlation plot of vglut1 and vglut3 immunofluorescence shows three populations: vglut1–pHluorin-transfected IHCs (arrowhead), vglut1-positive postsynaptic boutons (arrow), and nontransfected IHCs. C, Calibration of intravesicular pH using the ionophore FCCP. Confocal sections showing the fluorescence of vglut1–pHluorin-expressing IHCs in normal Ringer's solution (baseline) and when equilibrated to different pH with FCCP. Scale bar, 20 μm. D, Quantification of fluorescence in C, showing that resting fluorescence intensity corresponds to a pH of ∼6.5. The fluorescence of individual IHCs (red dots) at different pH was measured by defining an ROI encompassing the cytosolic region (excluding the nuclei) and normalized to the maximum intensity for each cell. These values are then averaged across all cells (black symbols).