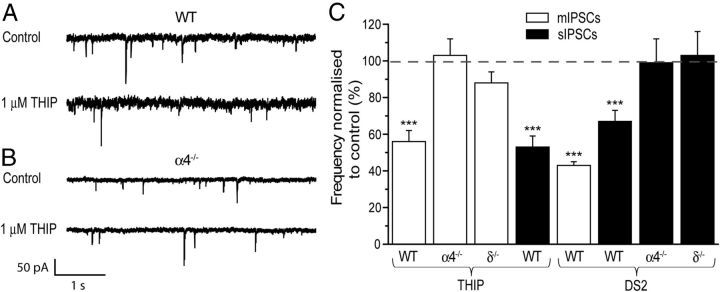
Figure 5.
α4βδ GABAARs influence GABA release onto MSNs. Representative traces of paired recordings of mIPSCs obtained from WT (A, top two traces) and α4−/− (B, bottom two traces) MSNs before and after THIP (1 μm). Note the decreased membrane noise associated with the α4−/− compare with the WT recording due to the reduced tonic conductance in the former. C, Histogram summarizing the effects of THIP (1 μm) expressed as a percentage of control, revealing this δ-selective agonist to produce a significant decrease in the mIPSC frequency of WT (n = 7), but not of α4−/− (n = 9) or δ−/− (n = 6) MSNs. THIP produced a similar reduction of the frequency of WT sIPSCs (n = 8). Similarly, DS2 (10 μm) decreased the frequency of mIPSCs (n = 7) and sIPSCs (n = 10) of WT MSNs, but not the sIPSC frequency of α4−/− (n = 8) or δ−/− (n = 6) MSNs. The bars (mIPSCs, white; sIPSCs, black) represent the mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 versus control by one-way repeated-measures ANOVA.