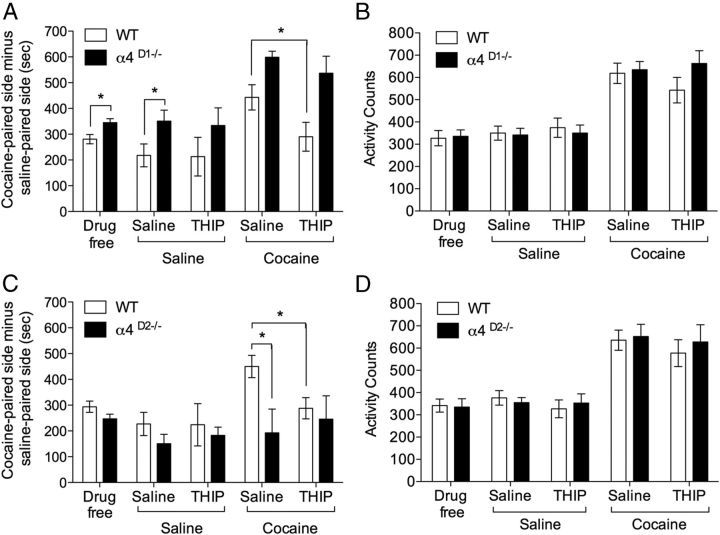
Figure 9.
CPP and locomotor activity in α4 cell-specific knock-out mice. A, Mice with α4 selectively ablated from D1-expressing neurons (α4D1−/−, n = 10) showed greater cocaine-induced CPP than WTs (n = 10). Systemic THIP had no effect on preference in either genotype (THIP/saline). A challenge dose of cocaine enhanced preference in both genotypes (saline/cocaine) and THIP blocked this enhancement in WT, but not α4D1−/− mice (THIP/cocaine). B, WT and α4D1−/− mice did not significantly differ in locomotor activity during CPP and activity was potentiated by a cocaine challenge in both genotypes. THIP (8 mg/kg, i.p.) did not alter activity during testing in either genotype. C, Cocaine induced CPP in both WT (n = 10) and mice with α4 selectively ablated from D2-expressing neurons (α4D2−/−, n = 10). However, the cocaine enhancement of preference seen in WT was not present in α4D2−/− mice (saline/cocaine). THIP blocked the cocaine enhancement in WT, but had no effect on performance in α4D2−/− mice (THIP/cocaine). D, Locomotor activity did not differ between WT and α4D2−/− mice during CPP and activity was potentiated by a cocaine challenge in both genotypes. THIP (8 mg/kg, i.p.) did not alter activity during testing in either genotype. *p < 0.05, post hoc comparisons.