Fig. 3. No increase in Tau-mediated toxicity caused by the R406W mutation.
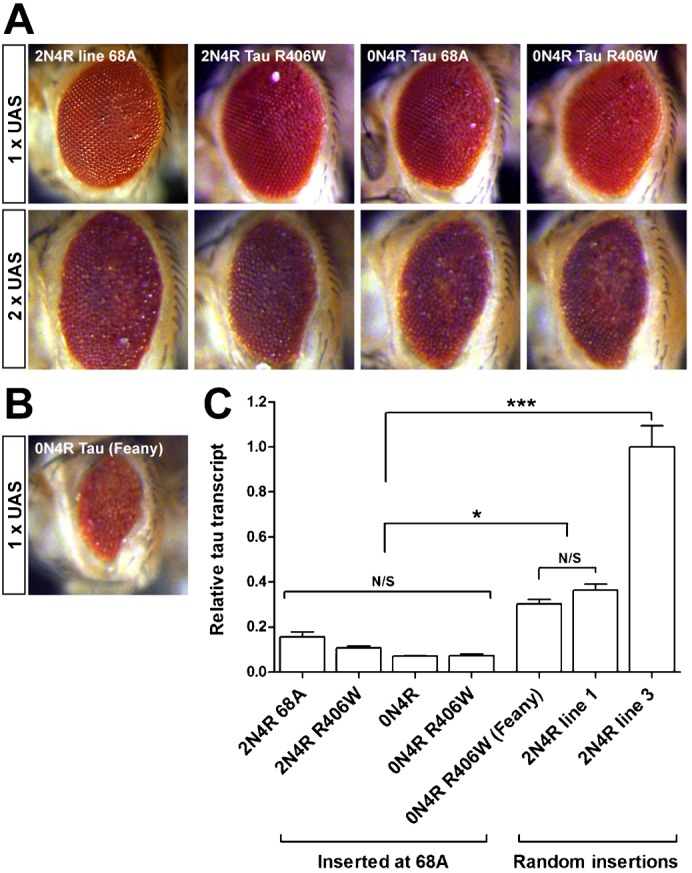
(A) GMR-gal4 driving expression from the 68A integration site of 2N4R or 0N4R Tau with or without the R406W mutations. Upper row: one copy of the UAS-insert. Lower row: two copies of the UAS-insert. GMR-gal4 is heterozygote in all cases. The R406W mutation does not increase toxicity. (B) GMR-gal4 driving 0N4R Tau R406W from a randomly inserted UAS-line generated by the Feany lab (Wittmann et al., 2001). (C) Tau transcripts levels driven by GMR-gal4 normalised to our random insertion line 3.
