Fig. 3. Association of ClC-5 with H+,K+-ATPase in hog gastric tubulovesicles.
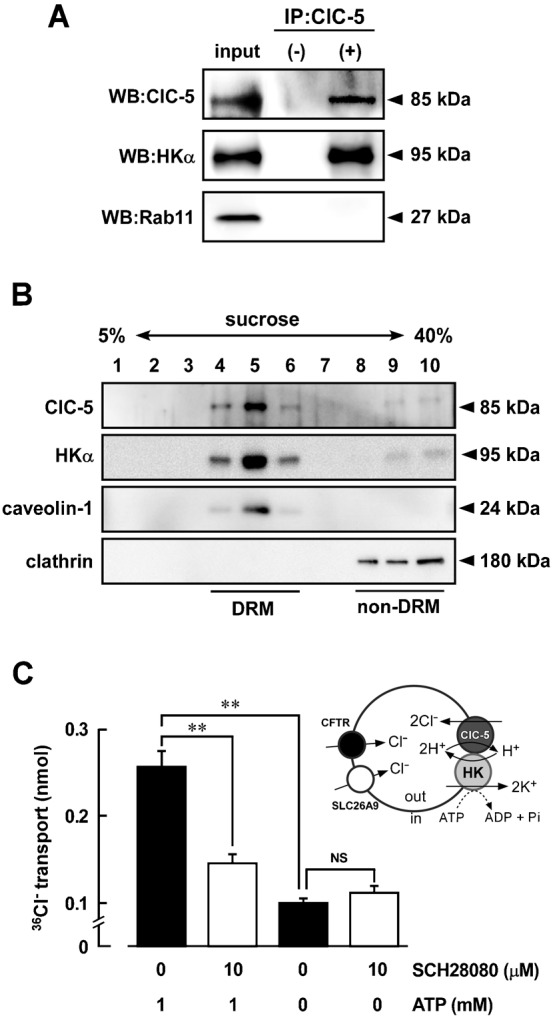
(A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with the detergent extracts of the hog gastric tubulovesicles (100 µg of potein) using anti-ClC-5 antibody (SS58) and protein A/G-agarose (IP: ClC-5, +). In control experiments, preimmune serum instead of the antibody was used (IP: ClC-5, −). The detergent extracts and immunoprecipitation samples were detected by Western blotting (WB) using antibodies for ClC-5 (SS58) labeled with HRP, HKα (1H9) and Rab11. The immunoprecipitation shown is representative of three independent experiments. (B) Detergent-resistant membrane (DRM) fractions and non-DRM fractions were isolated from hog gastric tubulovesicles by sucrose gradient (5–40%) as described in Materials and Methods. Western blotting was performed by using antibodies for ClC-5 (SS53), HKα (Ab1024), caveolin-1 and clathrin. (C) Inhibition of 36Cl− uptake into tubulovesicles by an inhibitor of H+,K+-ATPase (SCH28080). The 36Cl− uptake in tubulovesicles was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Effects of 1 mM ATP and/or 10 µM SCH28080 on the 36Cl− uptake were examined. As a control, the uptake was measured in the absence of ATP. n = 10. NS, not significantly different (P>0.05); **, significantly different (P<0.01).
