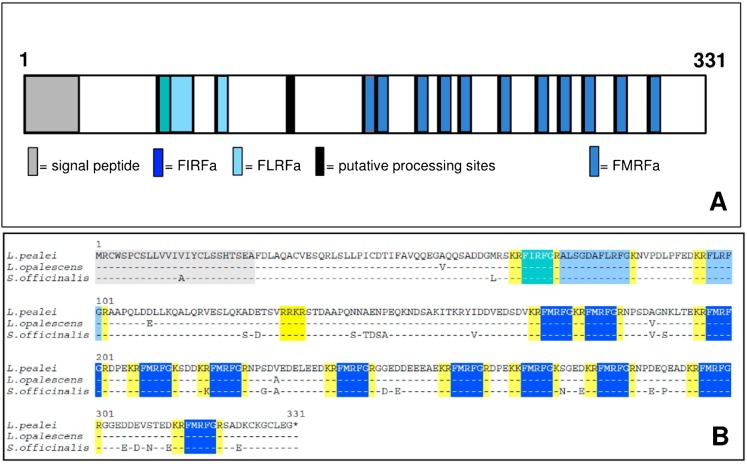
Fig. 1. Structure and amino acid sequence of the FMRFamide precursor of the squid Loligo pealei (L. pealei) and comparison to related decapodiforme species Loligo opalescens (L. opalescens) and Sepia officinalis (S. officinalis).
The amino acid sequence was deduced as the largest open reading frame from a 1692 nt transcript (GenBank accession number FJ205479.1). (A) The precursor contains eleven perfect FMRFG pentapeptide motifs (dark blue), one FIRFG sequence (green), and two FLMRFG motifs (light blue) of which one is extended at the N-terminus. The C-terminal glycine serves as substrate for amidation resulting in FMRFamide tetrapeptide. The motifs are flanked by pairs of basic amino acids (black) that are putative processing sites by prohormone convertase. The 25-amino acid signal peptide was predicted by SIG-Pred (Bradford, 2001) and SignalP (Nielsen et al., 1997) and is shown in grey. (B) Amino acid sequence of FMRFamide precursors of related cephalopods. Differences are shown. Amino acid sequences were translated from the nucleotide sequences entries AF303160.1 and Y11246.1.