Fig. 6.
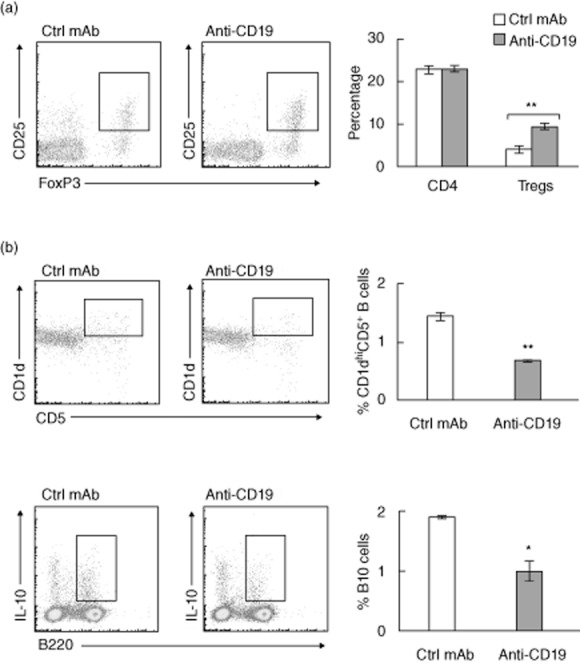
Effect of B cell depletion with anti-CD19 mAb on splenic CD4+ regulatory T cells (Tregs), CD1d+CD5+ B cell subset and B10 cells. (a) Increased frequency of splenic Tregs in B cell-depleted spontaneous autoimmune polyneuropathy (SAP) mice. Tregs were identified as CD4+CD25+forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3+) cells. Data summary includes two acute depletion and four pulse treatment experiments. **P < 0·0003 for %Tregs. (b) Effect of anti-CD19 mAb treatment on B220+CD1d+CD5+ cells and IL-10+ B cells (B10 cells) in spleens of SAP mice. Summary for B220+CD1d+CD5+ cells includes three acute depletion and three pulse treatments (12 weeks, **P < 0·0002). For B10 cells, splenocytes were stimulated for 4 h ex vivo with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (10 μg/ml) and leucocyte activation cocktail containing phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), ionomycin, brefeldin and BD Golgiplug prior to staining with anti-B220 and anti-interleukin (IL)-10 antibodies. *P < 0·003, n = 3 each. Bar graphs in (a) and (b) are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.).
