Fig. 1.
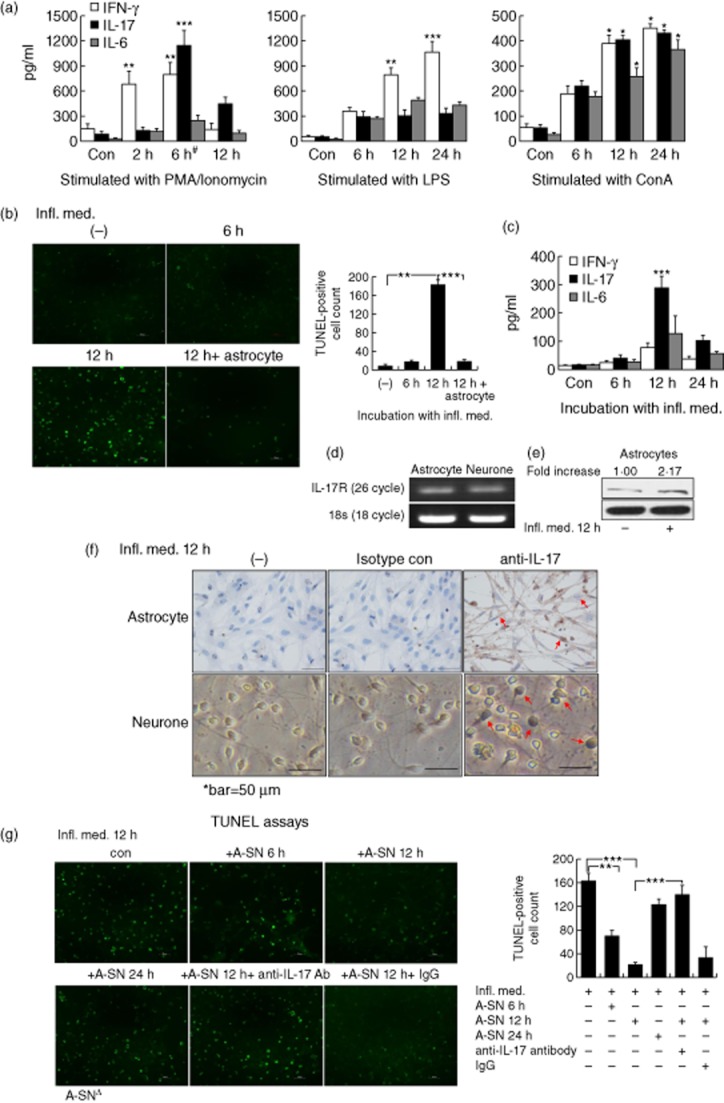
Neuronal protection effect of interleukin (IL)-17 in vitro (a) The peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were stimulated with 50 ng/ml phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) plus 1 μg/ml ionomycin, 100 ng/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or 5 μg/ml concanavalin A (ConA) for 6, 12 and 24 h. IL-17 in the supernatant were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). #The supernatant of PBMC stimulated by PMA/ionomycin for 6 h is referred to as ‘inflammatory media’ (Infl. Med). (b) The presence of astrocytes effectively protected primary cultured CGNs from apoptosis against stimulation with the half diluted inflammatory media by TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end-labelling) immunofluorescent assays. (c) The highest level of IL-17 was produced in the supernatant of the primary cultured astrocytes treated with the Infl. Med for 12 h. (d) The abundance of IL-17R expression in the CGNs (neurones) and astrocytes by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR). (e) The inflammatory media stimulated a significant increase on the expression of IL-17R expression in the astrocytes by Western blotting. (f) IL-17-positive staining in the primary cultured astrocytes or neurones (arrows) stimulated with the inflammatory media for 12 h by immunohistochemistry with an anti-IL-17 antibody, non-immune rabbit immunoglobulin (Ig)G was used as an isotype control. (g) IL-17 secreted by astrocytes protected neurones from apoptosis against the stimulation of the Infl. Med. The primary cultured neurones were stimulated with the Infl. Med. (half diluted) for 12 h with or without the supernatant of the astrocytes that were treated by the Infl. Med. for the indicated time-periods; additional anti-IL-17 neutralizing antibodies (20 ng/ml) were added where appropriate. All data are the means ± standard error of the mean of at least three experiments. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001; Δ, A-SN indicates the supernatant of astrocytes stimulated by the Infl. Med.
