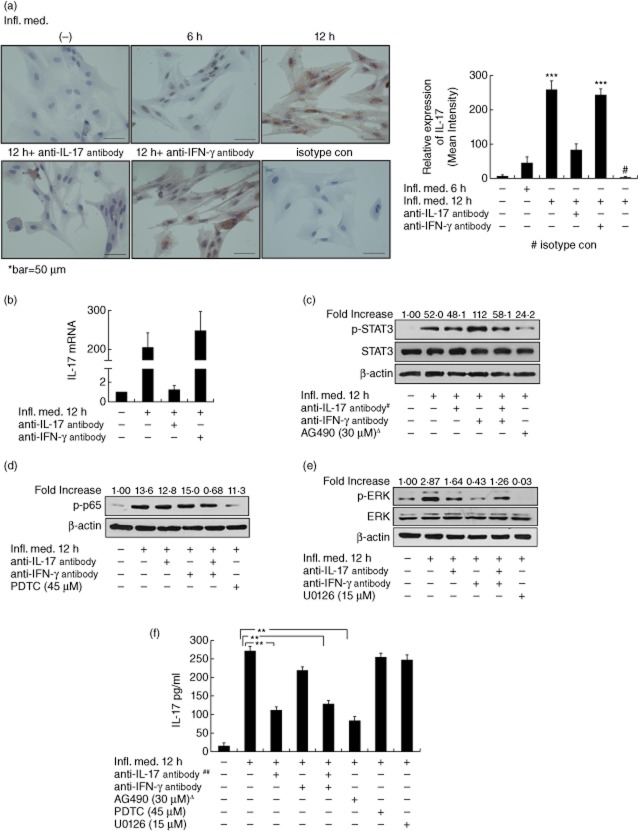
Fig. 4.
The role of interleukin (IL)-17 in the inflammatory media (Infl. Med). (a) IL-17-positive staining by immunochemistry with an anti-IL-17 antibody in astrocytes incubated with the Infl. Med. with different conditions. During the production of the Infl. Med. in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin, neutralizing anti-IL-17, or anti-interferon (IFN)-γ antibodies were added to decrease the level of IL-17 or IFN-γ, respectively, before the media were collected to stimulate the astrocyte culture. Immunoglobulin (Ig)G isotype control antibody was applied. (b) Relative expressions of IL-17 quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (qRT–PCR) in astrocytes stimulated with or without the Infl. Med. Multiple downstream signalling pathway activation including signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT-3) (c), p65, a subunit of nuclear factor (NF)-κB (d), or extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) (e) in astrocytes stimulated with different conditions. #The respective neutralizing antibodies were added during the production of the Infl. Med. to reduce the level of cytokine expression in the media. (f) IL-17 production by astrocytes stimulated with or without the the Infl. Med. with various conditions by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) assays. ΔRespective inhibitor drugs were added 2 h before, ##the antibodies 2 h after, the Infl. Med. application on the astrocytes for stimulation. All data are means ± standard error of the mean of at least three experiments. **P < 0·01.